Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses across the supply chain. By optimizing stock levels, companies can strike a balance between supply and demand, improving overall efficiency and reducing costs. One key metric used in inventory management is the number of days of inventory on hand, which determines how long a company's assets are tied up in stock.
The calculation of inventory days on hand is a vital tool for determining when to replenish stock. By tracking the average daily usage of inventory and the average inventory level, businesses can ensure that they have enough stock on hand to meet demand without excessive levels of inventory. This provides both cost savings through reduced storage and purchasing costs and better operational control.
Logistics plays a critical role in managing inventory days on hand. Efficient supply chain management ensures that inventory is replenished at the right time and in the right quantities. By optimizing transportation and warehousing operations, companies can reduce lead times and improve the overall flow of goods through the supply chain, ultimately reducing the number of days of inventory on hand.
Managing inventory days on hand also involves assessing the safety stock levels required to mitigate supply chain uncertainties. By considering factors such as demand variability and lead time variability, businesses can determine the appropriate buffer inventory needed to meet unexpected spikes in demand or delays in replenishment. This helps to ensure uninterrupted supply to customers and maintain high customer service levels.
In conclusion, controlling inventory days on hand is crucial for efficient inventory management. By calculating this metric and implementing effective strategies for stock replenishment, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Understanding Inventory Days on Hand
Inventory Days on Hand, also known as Days Sales of Inventory, is a key metric used in inventory management to measure how many days a company's inventory will last based on its current demand and supply. It provides valuable insight into the efficiency and effectiveness of a company's inventory management processes.
In order to calculate Inventory Days on Hand, you need to know the average daily demand and the average daily supply. The demand is the quantity of goods or products that customers are buying over a given period of time, while the supply is the quantity of goods or products that the company has available for sale.
Inventory Days on Hand can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a company's logistics, forecasting, and purchasing processes. If the number of days on hand is too low, it could indicate a potential risk of stockouts and lost sales. On the other hand, if the number of days on hand is too high, it could indicate excessive storage costs and tie up valuable assets in inventory.
Effective management of Inventory Days on Hand involves finding a balance between meeting customer demand and minimizing costs. By optimizing inventory levels, a company can improve cash flow, reduce carrying costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency. This can be achieved through various strategies such as just-in-time inventory management, safety stock calculations, and regular inventory turnover analysis.
In conclusion, Inventory Days on Hand is a vital measure for companies to monitor and control their stock levels. It provides insights into supply chain operations, helps in replenishment planning, and enables efficient inventory management. By understanding and managing Inventory Days on Hand effectively, companies can improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and maximize profitability.
What is Inventory Days on Hand?
Inventory Days on Hand, also known as Days of Supply or Days Inventory Outstanding, is a key performance indicator used by businesses to measure how long their stock would last based on current demand and stock levels. It provides insight into the efficiency of inventory management and operations.
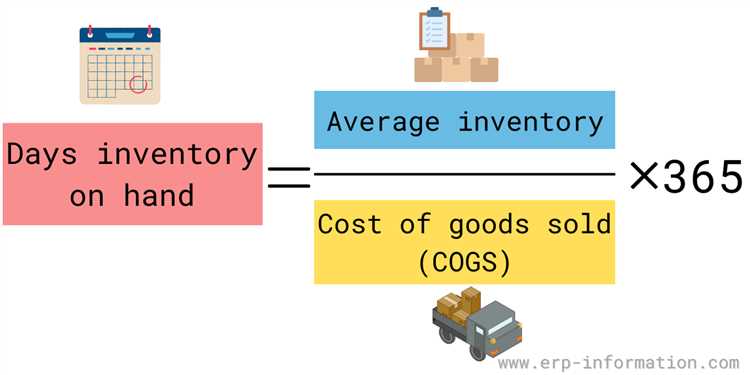
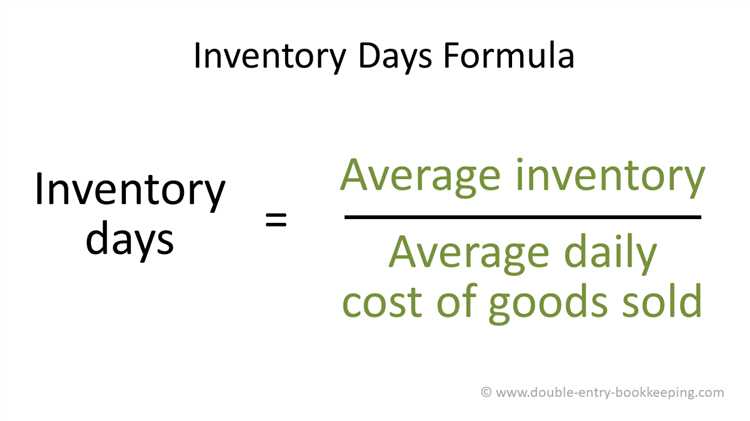
Inventory Days on Hand is calculated by dividing the average inventory value by the cost of goods sold per day. This metric helps businesses determine how many days they can maintain their current level of stock without replenishment.
Effective management of Inventory Days on Hand is crucial for businesses as it directly impacts their working capital, cash flow, and overall profitability. It helps them optimize their inventory levels, reduce excess stock, and prevent stockouts or backorders.
By monitoring and controlling Inventory Days on Hand, businesses can better plan their purchasing, production, and supply chain logistics. It allows them to align their inventory with customer demand, reduce costs associated with storage and obsolescence, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Forecasting demand accurately is essential for calculating and managing Inventory Days on Hand. By analyzing historical data, trends, and market conditions, businesses can make informed decisions regarding inventory replenishment, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking.
In conclusion, Inventory Days on Hand is a valuable metric for businesses to determine the optimal level of stock they should maintain. It helps them balance the costs associated with inventory management, ensure product availability, and maximize customer satisfaction.
Definition and Calculation
Inventory Days on Hand is a key metric used in supply chain management to evaluate the efficiency of stock levels and control inventory costs. It calculates the number of days for which a company's average inventory will be sufficient to meet customer demand.
The calculation of Inventory Days on Hand involves dividing the average inventory by the average daily cost of goods sold (COGS). The average inventory represents the average value of stock held by a company over a specific period, while the COGS represents the daily cost at which the company sells its products. The resulting value indicates the number of days a company can operate without needing to replenish its stock.
Efficient inventory management is crucial for businesses as it directly impacts their profitability. By accurately forecasting demand, companies can optimize their stock levels, reduce storage costs, and minimize the risk of stock-outs. Maintaining an optimal level of inventory allows companies to meet customer demand while minimizing tied-up assets and increasing turnover.
A higher number of Inventory Days on Hand indicates that a company has excess stock, leading to higher storage costs and increased risk of obsolescence. On the other hand, a lower number indicates inadequate stock levels, which can result in stock-outs and lost sales opportunities.
To optimize Inventory Days on Hand, companies often employ various strategies such as demand forecasting, efficient purchasing, and safety stock management. By accurately predicting demand, companies can align their replenishment processes and prevent overstocking or understocking. Safety stock, which is additional stock held as a buffer, helps companies mitigate supply chain disruptions and ensures continuous operations.
In conclusion, Inventory Days on Hand is a crucial metric for businesses to evaluate their stock levels and efficiency. By controlling inventory costs, optimizing turnover, and ensuring adequate supply, companies can enhance their operational performance and profitability.
The Importance of Inventory Days on Hand
Inventory Days on Hand refers to the number of days a company can sustain its operations based on its current stock levels. It is an essential metric that helps businesses in the supply chain management process, enabling them to understand the efficiency of their inventory control and replenishment processes.
By effectively managing the inventory days on hand, businesses can ensure they have the right amount of stock available to meet customer demand without experiencing stockouts or excessive inventory costs. It allows for better control over the flow of goods and materials within the supply chain, optimizing both purchasing and storage decisions.
Having a lower number of inventory days on hand indicates that a company has an efficient supply chain management system in place. This means that the company can quickly respond to changes in customer demand and avoid holding excessive stock, which ties up valuable assets and increases storage costs.
On the other hand, a higher number of inventory days on hand may indicate poor inventory turnover and inefficiencies in forecasting customer demand. This can result in higher storage costs, increased risk of obsolescence, and potentially lost sales opportunities. By monitoring and managing the inventory days on hand, companies can identify areas for improvement within their operations and make data-driven decisions to optimize their supply chain and reduce costs.
Effective inventory days on hand management also plays a crucial role in logistics and stock control. It enables businesses to streamline their operations, improve warehouse organization, and optimize procurement processes. By understanding the inventory turnover rate and adjusting stock levels accordingly, businesses can minimize lead times, improve overall efficiency, and ensure that stock is available when needed to fulfill customer orders.
In conclusion, inventory days on hand is a vital metric for businesses to monitor and manage. It provides insights into the efficiency of inventory control, helps in demand forecasting, and enables businesses to optimize their supply chain operations. By effectively managing inventory days on hand, companies can enhance their overall efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Optimizing Cash Flow
In today's competitive business environment, optimizing cash flow is essential for the success and sustainability of any organization. One area where companies can focus on to improve cash flow is inventory management. By effectively managing their stock levels, businesses can minimize tied-up cash in inventory and optimize their working capital.
One key aspect of optimizing cash flow is reducing inventory days on hand. Inventory days on hand is a measure of how many days a company's inventory will last based on its current sales rate. By keeping inventory days on hand low, companies can avoid excessive storage costs and free up cash that would otherwise be tied up in inventory.
To reduce inventory days on hand, companies need to have efficient replenishment processes in place. Accurate demand forecasting is crucial in order to determine the right quantity and timing of stock replenishment. By having the right amount of stock on hand, companies can avoid stockouts and minimize the need for emergency ordering, which can be costly and negatively impact cash flow.
Implementing effective safety stock control is another strategy for optimizing cash flow. Safety stock is a buffer stock that companies keep to meet unexpected changes in demand or supply disruptions. By setting appropriate levels of safety stock, companies can maintain customer service levels while also minimizing excess inventory that ties up cash.
Efficient supply chain operations and logistics are also essential for optimizing cash flow. By streamlining the purchasing and inventory management processes, companies can reduce lead times and eliminate unnecessary costs. This includes closely monitoring and managing supplier performance, negotiating favorable payment terms, and implementing lean inventory practices.
In conclusion, optimizing cash flow is a crucial aspect of successful business operations. By minimizing inventory days on hand, implementing effective replenishment and safety stock practices, and improving supply chain and logistics efficiency, companies can free up cash that can be reinvested in growth opportunities or used to improve overall profitability.
Reducing Holding Costs
Holding costs can significantly impact a company's bottom line. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to focus on reducing these costs by improving efficiency and implementing effective inventory management strategies.
One way to reduce holding costs is through accurate forecasting. By analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can better predict demand and adjust stock levels accordingly. This helps to avoid overstocking or understocking, ultimately reducing holding costs.
Another key factor in reducing holding costs is maintaining control over inventory and assets. Implementing strict inventory control measures, such as regular audits and tracking systems, allows businesses to identify and eliminate inefficiencies or inventory errors that can lead to excess stock and increased holding costs.
Effective logistics and storage management also play a significant role in reducing holding costs. Optimizing warehouse layouts and implementing efficient picking and replenishment processes can help minimize storage space requirements and improve inventory turnover. This, in turn, reduces the amount of stock held for extended periods, resulting in lower holding costs.
Furthermore, businesses can reduce holding costs by optimizing their supply chain management. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers and implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, businesses can minimize the need for excessive stockpiles and lower holding costs. This approach also helps to ensure a steady supply of inventory while reducing the risk of obsolescence or loss due to changes in demand.
Lastly, effective purchasing strategies can play a crucial role in reducing holding costs. By negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, businesses can reduce the cost of holding inventory. This includes negotiating shorter lead times for delivery, implementing flexible purchasing agreements, and exploring opportunities for consignment or vendor-managed inventory.
In conclusion, reducing holding costs requires a comprehensive approach that includes accurate forecasting, inventory control measures, efficient logistics and storage management, optimized supply chain management, and effective purchasing strategies. By implementing these strategies and continuously monitoring and adjusting inventory levels, businesses can minimize holding costs and improve their overall profitability.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
One key factor in improving customer satisfaction is reducing the number of days it takes to fulfill an order. By optimizing inventory levels and turnover, businesses can ensure they have the right amount of stock on hand to meet customer demand without tying up excessive capital in storage. This requires efficient inventory management and forecasting techniques to accurately predict and plan for customer demand.
Another aspect of improving customer satisfaction is having a streamlined logistics and supply chain operations. By implementing effective control and replenishment processes, businesses can ensure that their inventory is properly managed and replenished in a timely manner. This helps to avoid stockouts and delays in order fulfillment, ensuring that customers receive their products when they need them.
Efficiency in storage and asset management is also crucial for improving customer satisfaction. By optimizing warehouse layouts and implementing safety measures, businesses can reduce the time it takes to locate and retrieve stock items. This not only improves order fulfillment speed but also reduces the risk of damage to inventory, resulting in quicker and more accurate order delivery.
In addition, businesses can improve customer satisfaction by closely monitoring inventory turnover and demand patterns. By analyzing sales data and customer feedback, businesses can identify trends and adjust their inventory levels accordingly. This helps to minimize stock obsolescence and ensure that the right products are always available to meet customer demand.
Ultimately, improving customer satisfaction requires a holistic approach to inventory management. By implementing efficient and responsive purchasing, forecasting, and replenishment strategies, businesses can ensure that they always have the right products in stock and ready to ship. This enables them to provide a seamless and timely customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction levels and repeat business.
Factors Affecting Inventory Days on Hand
Inventory days on hand refers to the number of days a company's supply of assets or stock is expected to last. There are several factors that can affect this metric, which is an important measure of inventory management.
1. Demand Forecasting: Accurate forecasting of customer demand is crucial in determining the optimal number of inventory days on hand. This process involves analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and other factors to predict future demand.
2. Supply Chain Efficiency: The efficiency of a company's supply chain plays a vital role in inventory management. A well-organized and streamlined supply chain can reduce lead times and minimize stockouts, allowing for a lower number of inventory days on hand.
3. Inventory Turnover: The rate at which a company sells and replenishes its inventory, known as inventory turnover, also affects inventory days on hand. Higher turnover means products are moving quickly, resulting in shorter periods of holding inventory.
4. Safety Stock: Safety stock is a buffer inventory kept to meet unexpected increases in demand or delays in the supply chain. The level of safety stock maintained by a company can impact inventory days on hand. A higher safety stock level will increase the number of days of inventory on hand.
5. Purchasing and Control: Efficient purchasing practices and inventory control play a significant role in managing inventory days on hand. Effective control measures, such as proper stock counting and tracking methods, can help prevent inventory discrepancies and reduce the need for excessive stock levels.
6. Storage and Logistics: The efficiency of a company's storage and logistics operations can impact inventory days on hand. A well-organized warehouse system and effective logistics strategies can lead to faster inventory turnover and reduce the number of days inventory is held.
7. Costs: The costs associated with holding inventory, such as storage costs, insurance, and obsolescence, can affect inventory days on hand. Higher costs may incentivize companies to reduce their inventory levels, resulting in fewer days of inventory on hand.
In conclusion, managing inventory days on hand requires careful consideration of various factors, including demand forecasting, supply chain efficiency, inventory turnover, safety stock, purchasing and control practices, storage and logistics, and cost management. By optimizing these factors, companies can strive for greater efficiency and control in their inventory management processes.
Demand Variability
Demand variability is a significant factor in inventory management and control. It refers to the fluctuation in the demand for a product or service over a specific period of time. Understanding and managing demand variability is crucial for effective logistics and supply chain operations, as it directly impacts stock levels, costs, and customer satisfaction.
By accurately forecasting and analyzing demand variability, businesses can optimize inventory levels, avoiding both stockouts and excessive inventory. To ensure safety stock and efficient replenishment, organizations need to align their purchasing and storage operations with demand patterns. This involves implementing robust demand forecasting systems and utilizing real-time data to track and monitor changing consumer preferences.
Effectively managing demand variability can lead to improved efficiency in inventory management and reduced costs. By having an accurate understanding of demand patterns, businesses can reduce excess inventory, minimize storage costs, and optimize their supply chain operations. This also allows organizations to allocate resources more effectively and strategically, ensuring that the right products are available to customers at the right time.
Furthermore, demand variability impacts the overall efficiency of a company's operations. Excessive fluctuations in demand can lead to disruptions in the production and replenishment processes. This can result in stockouts, delays in order fulfillment, and increased lead times. By implementing effective demand variability management strategies, businesses can enhance their agility and responsiveness, mitigating the risks associated with unpredictable demand.
In summary, demand variability plays a critical role in inventory management and control. By effectively managing demand fluctuations, businesses can optimize their stock levels, reduce costs, and improve overall operational efficiency. This requires robust demand forecasting, efficient supply chain management, and strategic allocation of inventory assets. Ultimately, understanding and addressing demand variability can lead to improved customer satisfaction and a competitive advantage in the market.
Lead Time
Lead time is a crucial aspect of inventory control and management. It refers to the amount of time it takes for an inventory order to be fulfilled, from the moment it is placed to the moment it arrives in stock and is ready for use or sale. Efficient lead time management is essential for ensuring a smooth supply chain and optimal inventory levels.
Lead time is influenced by various factors, including supplier availability, transportation and logistics, production time, and storage and handling processes. A shorter lead time allows for faster inventory turnover and reduces the need for excessive stock levels, while a longer lead time can result in delays in replenishment and increased inventory holding costs.
To effectively manage lead time, businesses must accurately forecast demand and plan their purchasing and replenishment activities accordingly. This involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer preferences to estimate future demand. By implementing efficient supply chain and logistics strategies, businesses can minimize lead time and improve overall operational efficiency.
In addition to managing lead time, businesses also need to consider safety stock levels to account for unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply disruptions. Safety stock ensures that there is enough inventory on hand to meet customer demand during unforeseen circumstances. By maintaining optimal safety stock levels, businesses can minimize the risk of stockouts and customer dissatisfaction.
Overall, lead time management plays a crucial role in inventory control and effective supply chain management. By reducing lead time, businesses can improve their inventory turnover, optimize stock levels, and ensure timely availability of products to meet customer demand.
Order Frequency
The order frequency refers to how often a company places orders to replenish its inventory. It is a critical aspect of inventory management as it directly impacts the levels of stock on hand, safety stock, and overall operational efficiency.
Purchasing and supply chain operations need to carefully control the order frequency to ensure that the right amount of inventory is available at the right time. Ordering too frequently can lead to increased costs associated with transportation, storage, and handling. On the other hand, ordering too infrequently can result in stockouts, which can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers.
Efficient order frequency can be achieved through proper forecasting techniques and understanding of inventory turnover. By analyzing historical sales data and using accurate forecasting methods, companies can determine the optimal order frequency that balances the need for maintaining sufficient stock while minimizing holding costs.
Moreover, effective order frequency management requires collaboration between purchasing, operations, and logistics teams. Close coordination is necessary to align the ordering process with production schedules, transportation lead times, and storage capacities. By establishing clear communication channels and leveraging technology solutions, companies can streamline the order frequency and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Calculating Inventory Days on Hand
Calculating inventory days on hand is a crucial step in managing your stock levels effectively. It helps you determine the number of days your inventory will last based on your current stock levels and the average daily demand.
To calculate inventory days on hand, you need to know your average daily demand and your current inventory level. Start by calculating your inventory turnover, which is the number of times your inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period. Divide your cost of goods sold by your average inventory to get the turnover.
Next, divide the number of days in the period you want to calculate (such as a month or a quarter) by the inventory turnover. This will give you the number of days it takes for your inventory to turn over. Subtract this result from the average number of days it takes for your supplier to replenish your stock to get the inventory days on hand.
It's important to keep your inventory days on hand at an optimal level. If it is too high, it indicates excessive stock levels that tie up your working capital and increase storage costs. On the other hand, if it is too low, it can lead to stockouts and lost sales. By efficiently managing your inventory days on hand, you can strike a balance between meeting customer demand and minimizing holding costs.
Formula and Example
The formula for calculating inventory days on hand is a simple one: it is calculated by dividing the average inventory value by the cost of goods sold per day. This calculation provides a measure of how many days' worth of inventory a company has on hand at any given time.
For example, let's say a company has an average inventory value of $100,000 and a cost of goods sold per day of $10,000. Using the formula, we can calculate that the company has 10 days' worth of inventory on hand. This means that, on average, the company's inventory will last for 10 days before it needs to be replenished.
This calculation is crucial for logistics and inventory management. By understanding how many days' worth of inventory is on hand, a company can better plan its storage and supply chain operations. It helps to ensure that the company has enough inventory to meet customer demand, while also avoiding excess stock that can lead to higher costs, such as storage and holding costs.
Efficiency in inventory management is key. By closely monitoring inventory days on hand, companies can control their inventory levels more effectively. It allows for better forecasting of future demand, which in turn helps with optimizing purchasing decisions and reducing the risk of stockouts.
Furthermore, by calculating and managing inventory days on hand, companies can improve their overall asset turnover and financial performance. Having too much inventory on hand ties up valuable capital that could be invested elsewhere, while low inventory levels can lead to missed sales opportunities.
Managing Inventory Days on Hand
Inventory days on hand is an important metric for determining the time it takes for a company to sell its inventory. It is a measure of how quickly inventory is turned over and can help businesses assess the efficiency of their inventory management and control the costs associated with storage and purchasing.
To effectively manage inventory days on hand, businesses need to focus on safety stock levels and demand forecasting. Safety stock is a buffer quantity of inventory that is maintained to protect against uncertainty in demand or replenishment lead times. It ensures that a business has enough stock on hand to meet customer demand without incurring stockouts or delays in fulfillment.
Accurate demand forecasting is also crucial for managing inventory days on hand. By accurately predicting future sales and customer demand, businesses can optimize their inventory levels and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking. This can help improve operational efficiency and reduce costs associated with excess inventory or lost sales.
Another key factor in managing inventory days on hand is efficient replenishment and logistics. This involves optimizing the supply chain and ensuring smooth and timely delivery of inventory from suppliers to warehouses or stores. By improving the efficiency of the replenishment process, businesses can reduce lead times and inventory days on hand, leading to improved inventory turnover and cash flow.
Inventory management software can be a valuable tool in managing inventory days on hand. It can help businesses track and analyze inventory levels, forecast demand, and automate replenishment processes. This can save time and resources, improve accuracy, and provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and trends.
In conclusion, managing inventory days on hand is essential for businesses to balance operational efficiency, asset utilization, and customer satisfaction. By focusing on safety stock levels, accurate demand forecasting, efficient replenishment, and utilizing inventory management software, businesses can optimize their inventory turnover and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Forecasting and Demand Planning
Forecasting and demand planning play a crucial role in managing inventory levels and ensuring a smooth supply chain. By accurately predicting future demand, businesses can optimize their supply and storage strategies, minimize stockouts and overstocks, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Forecasting involves utilizing historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors to anticipate future demand for a product or service. Through forecasting, businesses can estimate the quantity and timing of inventory needed to meet customer demand. This knowledge enables efficient purchasing and replenishment processes, reduces lead times, and avoids unnecessary stock holding.
Demand planning is closely tied to forecasting and involves the strategic management of supply chain operations to meet customer demand. It includes activities such as inventory control, safety stock calculation, and turnover analysis. By effectively managing these aspects, businesses can optimize their inventory levels and ensure the availability of products when customers need them.
Efficient forecasting and demand planning also contribute to cost control and risk management. It helps businesses avoid excessive inventory levels that tie up working capital and increase storage costs. By accurately anticipating demand, businesses can also reduce the risk of stock obsolescence and minimize the need for costly expedited logistics processes.
In conclusion, forecasting and demand planning are critical components of inventory management. They enable businesses to optimize their supply chain operations, improve efficiency, and minimize costs. Through accurate prediction of demand and strategic inventory management, businesses can ensure that the right products are available at the right time, enhancing customer satisfaction and driving overall success.
Effective Inventory Management Strategies
Efficient inventory management strategies are vital for businesses that rely on maintaining adequate stock levels to meet customer demand. By implementing the right strategies, companies can optimize storage, ensure safety, and meet supply chain demands effectively.
One important strategy is forecasting, which involves analyzing past data and market trends to predict future demand. By accurately forecasting demand, businesses can avoid overstocking or understocking, ensuring that they have enough inventory on hand to meet customer needs.
Another crucial strategy is inventory turnover, which involves managing the flow of goods in and out of the warehouse. By monitoring turnover rates, businesses can identify slow-moving or obsolete items and take appropriate actions, such as discounts or promotions, to sell them quickly and free up space for more in-demand products.
Purchasing and replenishment strategies also play a significant role in effective inventory management. It is essential to establish strong relationships with suppliers and ensure timely delivery of goods. By streamlining the purchasing process and setting up efficient logistics, businesses can minimize stockouts and reduce lead times.
Effective control and management of inventory levels are essential to optimize storage space and minimize costs. By implementing inventory control systems, businesses can track stock levels, set reorder points, and automate the replenishment process. This not only helps in maintaining the right quantity of stock but also reduces the risk of stockouts and excess inventory.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider safety in inventory management strategies. Proper storage, handling, and labeling of goods help minimize the risk of accidents and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Regular audits and inspections can identify any potential hazards and allow for timely corrective actions.
In conclusion, effective inventory management strategies involve forecasting, supply chain management, and control of stock levels. By implementing these strategies, businesses can optimize the flow of goods, minimize costs, and ensure customer satisfaction.
Utilizing Technology and Automation

In order to improve efficiency and replenishment in your supply chain, it is crucial to leverage technology and automation. By implementing advanced systems and tools, you can streamline the process of inventory turnover, logistics, and control.
For instance, using automated software can help you keep track of inventory levels and alert you when it's time to re-order. This eliminates the need for manual hand counting and reduces the risk of errors. Additionally, automation can facilitate storage and organization, ensuring that your assets are properly managed and easily accessible.
Another benefit of utilizing technology in inventory management is the ability to forecast demand accurately. By analyzing historical data and trends, you can make informed decisions about purchasing and stock levels. This helps to prevent stockouts and overstocks, maximizing your supply chain efficiency.
Furthermore, technology can improve the safety of your inventory by implementing barcode scanning or RFID tagging systems. This allows for better tracking and tracing of products, reducing the risk of theft or loss. By enhancing safety measures, you can protect your assets and maintain optimal inventory levels.
In summary, technology and automation play a vital role in inventory management. They enable better control, increased efficiency, accurate forecasting, and improved safety. By embracing these tools, you can enhance your operations and ensure that your supply chain runs smoothly.