Backorder is a term that is commonly used in the business world. It refers to a situation where a customer has placed an order for a product, but the company is unable to fulfill the order immediately due to various reasons. These reasons can include a lack of stock, production delays, or high demand for the product. Understanding the meaning of backorder is of utmost importance for both businesses and customers alike.
The importance of understanding backorder lies in the fact that it allows businesses to effectively manage their inventory and customer expectations. By understanding why a product is backordered, businesses can take appropriate measures to address the issue, such as ordering more stock or expediting production. This can help minimize the impact on customer satisfaction and maintain a positive brand image.
From a customer's perspective, understanding backorder makes sense as it provides insight into the status of their order. It gives them a clear understanding that their order will be fulfilled, but it may take some time. This knowledge allows customers to plan accordingly and make informed decisions about their purchase.
In the context of supply chain management, backordering has a specific definition. It refers to the practice of accepting orders for goods or services that are temporarily out of stock, with the intent to fulfill them at a later point. This clarification is important as it differentiates backordering from the cancellation of orders or inability to fulfill them entirely.
The meaning and purpose of backorder hold significant significance for businesses operating in today's fast-paced and competitive market. It helps them navigate the challenges of demand and supply fluctuations, maintain customer loyalty, and keep their operations efficient. In conclusion, understanding the interpretation and meaning of backorder is vital for both businesses and customers to ensure a smooth and satisfactory ordering experience.
What is a Backorder?
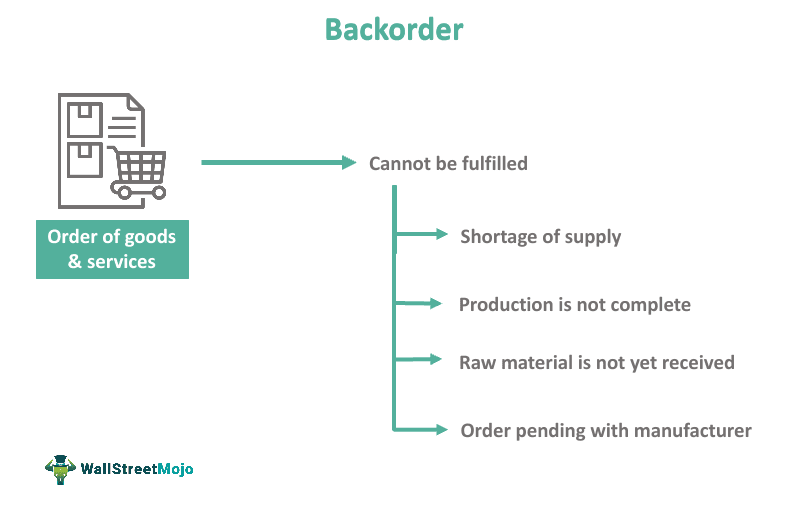
A backorder refers to an order that cannot be fulfilled at the current time and is therefore placed on hold until the product or item becomes available in the future. Backordering occurs when a customer places an order for a product that is out of stock or not currently available for delivery. It is a common practice in the business world, especially in manufacturing and retail industries, to manage customer expectations and maintain a smooth order fulfillment process.
When a product is backordered, it means that the customer's request for the item has been received and acknowledged by the seller, but due to certain circumstances, the order cannot be immediately processed or shipped. The reasons for backorders may vary, including manufacturing delays, supplier shortages, high demand exceeding supply, or logistical issues. It is important for both buyers and sellers to have a clear understanding of the concept of backordering in order to effectively manage customer inquiries and meet expectations.
The significance of backorders lies in the fact that they represent unfulfilled orders that require attention and clarification. From the customer's point of view, a backordered item may be of great importance and have a specific meaning or interpretation. For example, it could be a critical component for their ongoing project or a desired product that is not readily available from other sources. On the other hand, from the seller's perspective, managing backorders is crucial to maintaining customer satisfaction, building trust, and ensuring business continuity.
In summary, a backorder can be defined as an order that cannot be immediately fulfilled due to unavailability of the product or item. It is important to understand the concept, reasons, and implications of backordering in order to effectively manage customer inquiries and maintain a smooth order fulfillment process.
Definition of Backorder
A backorder is a situation that occurs when a customer places an order for a product that is currently not in stock or unavailable. In a nutshell, it is a point in the order fulfillment process where a customer may have to wait for the desired product to become available again.
The definition of backorder is of utmost importance because it provides a clear understanding of the concept. Backorders typically happen when there is high demand for a certain product and the supplier or retailer is unable to meet the current level of demand.
It is worth noting that a backorder can also be viewed as an importquiry to the supplier or retailer, as it reflects the customer's interest and desire to purchase the product despite its unavailability at the moment. In this sense, backordering can serve as a valuable indicator of customer demand and market trends.
The purpose of backorder clarification is to provide customers with an explanation and update regarding the status of their order. It is essential for effective communication between the retailer and the customer to ensure transparency and customer satisfaction.
The significance and meaning of backorder lie in its interpretation as a temporary delay or unavailability of a product. Customers may choose to backorder an item due to its popularity, limited availability, or other reasons. Understanding the concept of backorder allows businesses to better manage and plan their inventory and supply chain processes.
Common Causes of Backorders
When it comes to the interpretation and understanding of backorders, it is important to consider their purpose and definition. A backorder occurs when a customer places an order for a product that is temporarily out of stock. The significance of backorders lies in their importance for businesses to fulfill customer demands and maintain customer satisfaction.
There are several reasons why backorders may occur. One common reason is an unexpected increase in demand for a particular product. This could be due to a sudden surge in popularity or a marketing campaign that generates significant interest. In such cases, businesses may find themselves unable to keep up with the sudden influx of orders, leading to backordered items.
Another reason for backorders is supply chain disruptions. This could include delays from suppliers or logistical challenges that impact the timely delivery of products. When these issues arise, businesses may have to rely on backordering to fulfill orders until the supply chain can be restored.
Furthermore, backorders can also be caused by inaccurate inventory management. If businesses do not have an accurate understanding of their stock levels, they may inadvertently accept orders for products that are not in stock. In these cases, backorders serve as a means of clarification and allow businesses to communicate with customers regarding the delay in fulfilling their orders.
In conclusion, the common causes of backorders include unexpected spikes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and inaccurate inventory management. Understanding the meaning and import of backordering is essential for businesses to effectively manage customer expectations and maintain a high level of customer satisfaction.
The Impact of Backorders on Businesses
When it comes to business operations, backorders can have a significant impact. Understanding the meaning and definition of backorders is crucial in order to grasp their purpose and significance.
A backorder refers to an order that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to insufficient stock or unavailability of a product. This may occur when the demand for a particular item exceeds the supply, leading to a delay in delivery.
The impact of backordering on businesses can be both positive and negative. On one hand, it can be a sign of high demand and popularity for a product. This can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, as they are willing to wait for the product to become available.
However, backorders can also have negative implications. It can lead to frustrated customers who may cancel their orders or seek alternatives elsewhere, resulting in lost sales. Moreover, backorders can disrupt the supply chain and create delays in other operations.
Businesses need to effectively manage and communicate backorders to minimize the negative impact. Providing clear importquiry and clarification regarding the reason for the backorder is crucial. Timely updates and explanations on the expected availability of the product can help in managing customer expectations and avoiding dissatisfaction.
Interpretation and understanding of the reasons behind backorders are also important for businesses. It allows them to identify and address the root causes, such as issues in production or supply chain management, to prevent recurring backorders in the future.
In conclusion, the impact of backorders on businesses varies depending on how they are managed. The meaning and significance of backorders lie in their ability to reflect customer demand while also presenting challenges in meeting that demand. By effectively managing backorders and communicating with customers, businesses can minimize negative impacts and optimize their operations.
Financial Consequences of Backorders
Understanding the financial consequences of backorders is of utmost importance for businesses engaged in backordering. It is crucial to have a clear clarification and definition of what a backorder is in order to grasp the financial implications associated with it. Backorders occur when a customer places an order for a product that is currently out of stock or unavailable. The reason behind the backorder could be a delay in production, a shortage in materials, or high demand for the product.
The financial consequences of backorders can vary depending on the interpretation and understanding of the term. However, the most common financial impact is an increase in costs. When an item is backordered, businesses may incur additional expenses such as rush orders, expedited shipping, or overtime pay to fulfill the order as quickly as possible.
Another financial consequence of backorders is the potential loss of customer loyalty. If customers repeatedly experience backorders, they may become frustrated and turn to competitors who can meet their demands promptly. This can lead to a decrease in sales and revenue for the business.
Furthermore, backorders can also disrupt supply chain operations and inventory management. Businesses may need to allocate additional resources to manage backorders, resulting in inefficiencies that can impact the overall profitability of the organization.
In summary, the financial consequences of backorders extend beyond the immediate loss of a single sale. It is essential for businesses to understand the importquiry of backorders and develop strategies to minimize their occurrence and mitigate their negative impact on the company's financial performance.
Customer Relations and Backorders
Customer relations play a crucial role when dealing with backorders. When a product is backordered, it means that there is a delay in fulfilling an order due to lack of available stock. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and frustration.
It is important for businesses to communicate with their customers regarding the status of their backorder. Providing an importinquiry with regular updates and a clear explanation of the reason for the delay can help maintain customer satisfaction and build trust.
Customers often seek clarification on the meaning and significance of a backorder. Providing a concise definition and explanation of what a backorder is can help customers understand the situation and the impact it may have on their order.
Furthermore, businesses should emphasize the importance of their customers' understanding and point out the purpose of having a backorder system in place. This can include highlighting the significance of managing inventory and fulfilling orders in a timely manner.
Another important aspect of customer relations when dealing with backorders is offering alternatives or solutions to the customer. This can include providing options for partial shipments, offering similar products, or giving the customer the choice to wait for the backordered item to become available.
In summary, good customer relations are crucial in managing backorders effectively. By providing clear explanations, regular communication, and offering alternatives, businesses can help mitigate customer dissatisfaction and maintain strong relationships with their customers.
Strategies for Managing Backorders

When it comes to managing backorders, it is important to have a clear understanding of what they mean and their significance. Backorders occur when a customer places an order for a product that is currently out of stock or unavailable. The key point to remember is that a backorder is not a cancellation or a lost sale, but rather a commitment to fulfill the order as soon as the product becomes available.
One strategy for managing backorders is to provide regular updates and clear communication to customers about the status of their backordered items. This helps to build trust and keeps customers informed about when they can expect to receive their products. Providing an estimated time of arrival or expected ship date can give customers a sense of certainty and allow them to plan accordingly.
Another important strategy is to prioritize the fulfillment of backorders. This means allocating inventory and resources to fulfill backorders before fulfilling new orders. By doing so, businesses can prioritize customer satisfaction and ensure that customers who have placed orders first receive their products in a timely manner.
Additionally, it may be beneficial to offer alternatives or substitutions for backordered items. This can help meet the needs and expectations of customers while still fulfilling their order. Providing options and keeping customers informed about any changes or substitutions can help minimize frustrations and maintain customer satisfaction.
Finally, it is essential to regularly review and analyze backorder data to identify any recurring patterns or trends. This can help businesses understand the reasons behind backorders and take proactive measures to prevent them in the future. By analyzing data, businesses can make informed decisions about inventory management, production planning, and supply chain optimization.
Inventory Management Techniques

Understanding and implementing effective inventory management techniques is of utmost importance for any business that deals with a physical product. Proper inventory management ensures that a company has the right amount of stock on hand to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
One inventory management technique is the ABC analysis, which involves classifying items into three categories based on their importance. This helps in prioritizing items and allocating resources accordingly. Another technique is the just-in-time (JIT) inventory system, where inventory is ordered and received just in time for production. This minimizes the amount of inventory held, reduces storage costs, and improves cash flow.
An explanation of inventory management techniques can also include the interpretation of backorder. When a product is backordered, it means that the item is currently out of stock and customers will have to wait for it to become available. The reason for backordering could be due to unexpected demand, supplier issues, or production delays. It is important for businesses to clarify the backordered status to customers and provide them with a clear timeline for fulfillment.
Another inventory management technique is economic order quantity (EOQ), which determines the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. By calculating the EOQ, businesses can find the balance between ordering too much inventory, resulting in higher carrying costs, or ordering too little inventory, leading to stockouts and lost sales.
In summary, inventory management techniques play a crucial role in maintaining a well-managed and cost-effective supply chain. Understanding the various techniques and their purpose can help businesses optimize their inventory levels, meet customer demand, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Communication and Transparency
Effective communication is of utmost importance when it comes to the backordering process. It is essential for businesses to maintain transparency and provide clear explanations for the reasons behind a product being backordered. This helps in ensuring that customers have a clear understanding of the situation and can make informed decisions.
Transparency plays a significant role in the interpretation and understanding of backorders. It assists in clarifying the meaning and sense of backordering, as well as the purpose and importance of the process. By communicating openly, businesses can ensure that customers know the reasons behind the backorder and the estimated timeframe for the fulfillment of their order.
A clear definition and explanation of backordering can prevent any confusion or misinterpretation. Businesses can provide an importinquiry point for customers, where they can find detailed information about the backordered products and the reasons for the delay. This enables customers to understand the significance of their backorder and make informed decisions regarding their purchase.
Furthermore, by maintaining open communication and transparency, businesses can build trust with their customers. When customers feel well-informed about the backorder process, they are more likely to have patience and understanding. This can lead to stronger customer relationships and increased customer loyalty.
In summary, effective communication and transparency are essential in the context of backorders. By providing clear information and explanations, businesses can ensure that customers have a thorough understanding of the backordering process. This helps in preventing confusion, building trust, and maintaining strong customer relationships.
Collaborating with Suppliers
When it comes to backordering, collaborating with suppliers is of utmost importance. Suppliers play a crucial role in the backorder process, as they are responsible for fulfilling orders that cannot be immediately met due to stock unavailability. A strong collaboration between buyers and suppliers is essential to ensure the timely delivery of backordered items.
The purpose of collaborating with suppliers in the context of backordering is to find a sense of mutual understanding and to work together towards a solution. Suppliers can provide valuable insights into the reasons behind backorders, such as production delays, inventory management issues, or unexpected spikes in demand.
To effectively collaborate with suppliers, it is necessary to communicate clearly and seek clarification on the meaning and interpretation of backordered items. This includes understanding the significance of the backorder status, the import of the backorder notification, and the expected timeframe for fulfillment.
Collaboration also involves actively engaging with suppliers to address inquiries and concerns related to backorders. It is important to point out any specific requirements or changes to the original order to ensure accurate and timely delivery of backordered items.
In summary, collaborating with suppliers is of paramount importance in the backorder process. It allows for a clearer understanding of the backorder situation, facilitates problem-solving, and ensures a smoother flow of operations between buyers and suppliers.
Best Practices for Avoiding Backorders
When it comes to avoiding backorders, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the meaning and significance of backordering. It is important to start with a clear definition and interpretation of backorders to fully comprehend its import.
Backorder, by definition, refers to an order that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to a lack of available stock. It is a situation where the requested items are not currently in inventory and need to be replenished or produced. So, to avoid backorders, a company needs to ensure that it has enough products in stock to meet customer demands.
An explanation for the occurrence of backorders can be attributed to various reasons. Some may include issues with the supply chain, delays in production or delivery, unexpectedly high demand, or inaccurate inventory management. Regardless of the specific reason behind backorders, the importance of avoiding them cannot be overstated.
To clarify, backordering can have significant consequences for businesses. It can lead to dissatisfied customers, lost sales opportunities, damage to reputation, and decreased customer loyalty. Therefore, companies must implement best practices to minimize backorders and maintain a seamless order fulfillment process.
- Improve forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting allows companies to anticipate future needs and plan their inventory accordingly. This practice helps prevent inventory shortages and subsequent backorders.
- Effective inventory management: Regular monitoring and tracking of inventory levels are essential to identify potential stock shortages. Implementing automated inventory management systems can streamline this process and reduce the likelihood of backorders.
- Collaborate with suppliers: Building strong relationships and open communication with suppliers can help ensure a steady supply of products. This collaboration allows companies to handle unexpected surges in demand more effectively.
- Priority on stock replenishment: Companies should prioritize the fulfillment of backordered items as soon as possible. This prevents further delays and minimizes the impact on customer satisfaction.
- Constantly review and optimize processes: Regular evaluation of order fulfillment processes can uncover areas for improvement. Streamlining these processes can reduce the chances of backorders and enhance overall efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding and actively avoiding backorders is crucial for businesses to maintain customer satisfaction, reputation, and profitability. Implementing the mentioned best practices can help companies minimize the occurrence of backorders and ensure a smooth order fulfillment experience.
Forecasting and Demand Planning
Forecasting and demand planning are crucial processes in supply chain management. They involve predicting future demand for a product or service in order to effectively plan production and inventory levels. A thorough understanding of these processes is of great importance for businesses, as it allows them to meet customer demands and optimize their operations.
Forecasting involves the estimation of future demand based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It provides an explanation of the expected demand in terms of quantities and timing. On the other hand, demand planning involves analyzing the forecasted demand and developing strategies to meet that demand in the most efficient way.
The significance of forecasting and demand planning is evident in the context of backordered items. When an item is backordered, it means that it is currently out of stock but can be ordered by customers for future delivery. The reason for backordering may vary, such as unexpected demand spikes or production delays. By accurately forecasting and planning demand, businesses can minimize the occurrence of backordered items, reducing customer dissatisfaction and lost sales.
Forecasting and demand planning serve the purpose of ensuring that businesses have the right amount of inventory at the right time. It is of utmost importance in industries with seasonal demand patterns or unique events that can affect demand. Through careful analysis and interpretation of data, businesses can make informed decisions about production, inventory management, and supply chain strategies.
In summary, forecasting and demand planning are essential for businesses to effectively manage their supply chains and meet customer demands. They provide a sense of direction and purpose in the face of uncertainty, helping businesses minimize backorders and optimize their operations. Understanding the definition, meaning, and importance of these processes is key to achieving success in today's competitive market.
Safety Stock and Reorder Point Strategies
When it comes to managing backordered items, implementing effective safety stock and reorder point strategies becomes crucial. Safety stock is a buffer quantity of inventory that is maintained to protect against uncertainties in demand and supply. The purpose of safety stock is to ensure that there is enough inventory available to fulfill customer orders even during unforeseen circumstances.
Reorder point, on the other hand, is the inventory level at which a new order needs to be placed with the supplier to replenish the stock. It is calculated based on factors such as lead time, demand, and safety stock levels. The reorder point serves as a trigger for initiating the procurement process.
It is important to understand the significance of safety stock and reorder point in the context of backordering. Safety stock allows businesses to have a cushion against unpredicted fluctuations in demand or delays in supply. By maintaining a certain level of safety stock, businesses can minimize the risk of stockouts and backorders.
The calculation and interpretation of the reorder point also play a vital role in effective inventory management. It helps businesses determine the right time to place an order to replenish the inventory and avoid stockouts. A well-calculated reorder point ensures that the inventory levels are optimized, preventing excess inventory and potential losses.
Both safety stock and reorder point strategies contribute to better understanding and management of backorders. They provide a framework for businesses to maintain a balance between stock availability and stock holding costs, optimizing their inventory management practices. Implementing these strategies requires careful analysis, considering factors such as product demand patterns, supplier lead times, and customer expectations.
Continuous Improvement and Process Optimization
Backordering is a concept that requires further clarification and explanation. It refers to a situation where a customer places an order for a product that is currently out of stock or unavailable. Understanding the meaning and definition of backorder is of utmost importance for businesses, as it highlights the significance and purpose of improving and optimizing their processes.
In the context of continuous improvement and process optimization, backordered items serve as an importquiry point for businesses. By interpreting and understanding the reason behind backorders, companies can identify areas of their operations that require improvement. It provides an opportunity to analyze the sense and purpose behind these orders, allowing businesses to take proactive measures to prevent future instances of backordering.
Continuous improvement and process optimization are crucial for reducing the occurrence of backorders. By examining the backorder data, companies can identify patterns and trends, enabling them to make informed decisions and implement strategies to minimize the likelihood of backorders in the future. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs associated with backorder fulfillment.
Therefore, continuous improvement and process optimization play a pivotal role in addressing the challenges posed by backorders. Through a proactive approach, businesses can ensure that they meet customer demands and expectations seamlessly, thereby fostering growth and improving their overall competitiveness in the market.
Tools and Technology for Backorder Management
Importquiry: An important tool for backorder management is importquiry, which allows companies to track and manage the import of goods. It helps in keeping track of orders, understanding their interpretation, and providing the necessary clarification.
Order Management Systems: Order management systems provide a comprehensive explanation of backorders. They help in defining the backorder and its significance, giving a clear understanding of its meaning and purpose. These systems also assist in managing backordered items and their delivery.
Inventory Management Software: Inventory management software plays a crucial role in backorder management. It helps in keeping track of backordered items, their availability, and the reason for their backordering. It also helps in determining the point at which additional inventory needs to be ordered to avoid backorders.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: CRM software helps in maintaining strong relationships with customers by providing timely updates on backorders. It allows companies to communicate the reason for the backorder, its expected delivery date, and any changes in the status. This ensures transparency and customer satisfaction.
Sales Analysis Tools: Sales analysis tools can provide valuable insights into the reasons for backorders. They help in analyzing sales patterns, identifying potential bottlenecks in the supply chain, and making informed decisions to minimize backorders in the future.
Collaboration and Communication Tools: Backorder management often involves collaboration and communication with various stakeholders, including suppliers, distributors, and customers. Collaboration and communication tools facilitate effective communication, enabling timely updates, clarification, and coordination to resolve backorder issues efficiently.
Inventory Management Software
Definition: Inventory management software is a tool that helps businesses track and manage their inventory, including the goods they have on hand, on order, and in transit.
Meaning: The meaning of inventory management software lies in its ability to provide businesses with a comprehensive and real-time view of their inventory, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding stock levels, ordering, and fulfillment.
Explanation: By utilizing inventory management software, businesses can effectively track and analyze their inventory, ensuring that they have the right amount of stock available at the right time. The software provides detailed information on each item, including its current quantity, location, and availability, allowing businesses to avoid overstocking or running out of crucial products.
Backordered: When an item is backordered, it means that it is currently out of stock but is expected to be replenished in the future. Inventory management software enables businesses to track backordered items, ensuring that they can fulfill customer orders as soon as the stock becomes available.
Importance: The importance of inventory management software cannot be overstated, as it allows businesses to optimize their inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve customer satisfaction. By understanding the current status of their inventory, businesses can avoid stockouts, delays, and overspending on unnecessary stock.
Understanding: A clear understanding of inventory management software is essential for businesses that want to efficiently control their inventory. It enables them to plan and execute procurement strategies, streamline order processing, and meet customer demands with minimal disruptions.
Significance: The significance of inventory management software lies in its ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall profitability. By effectively managing their inventory, businesses can free up capital, reduce waste, and optimize their supply chain.
Order: Inventory management software plays a crucial role in managing the order fulfillment process. It enables businesses to ensure that customer orders are fulfilled promptly and accurately, minimizing delays and improving customer satisfaction.
Clarification: Inventory management software provides clarity and transparency in terms of stock levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding replenishment, pricing, and promotions. It ensures that businesses have the necessary information to meet customer demands and optimize their inventory management strategies.
Backordering: The concept of backordering refers to the practice of accepting customer orders for products that are currently out of stock but will be fulfilled once the stock becomes available. Inventory management software allows businesses to efficiently manage the backordering process, ensuring that customer orders are prioritized and fulfilled in a timely manner.
Point: The point of using inventory management software is to streamline and automate inventory-related processes, ultimately improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. It serves as a central hub for all inventory-related information, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their operations.
Importquiry: Inventory management software enables businesses to automate inventory inquiries, allowing employees to quickly access real-time stock information, check availability, and provide accurate responses to customer inquiries. This not only improves customer service but also reduces the time and effort required to handle inventory-related inquiries.
Overall, inventory management software is a valuable tool for businesses looking to optimize their inventory management processes. By providing a clear and accurate view of inventory, it helps businesses make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and meet customer demands effectively.
Supply Chain Analytics
Supply chain analytics is the process of analyzing data and information related to the supply chain with the goal of understanding and improving its performance. It involves the use of various techniques and tools to gather, interpret, and visualize data in order to gain insights and make informed decisions.
The significance of supply chain analytics lies in its ability to provide a sense of clarity and purpose to the complex and interconnected network of activities that make up a supply chain. By understanding the meaning and interpretation of different data points, organizations can identify areas of improvement, detect inefficiencies, and optimize their operations.
One of the key purposes of supply chain analytics is to gain a better understanding of backorder situations. A backorder occurs when a customer places an order for a product that is currently out of stock or unavailable. By analyzing data on backorders, organizations can identify the reasons behind them, such as supply chain disruptions, production delays, or unexpected increases in demand.
The importquiry of backorders lies in their impact on customer satisfaction and overall business performance. Understanding the reasons for backordered items can help organizations take corrective actions to minimize their occurrence and optimize inventory levels.
Supply chain analytics also plays a crucial role in backordering decisions. By analyzing historical data and demand patterns, organizations can determine when to place backorders for certain products and in what quantities. This helps ensure that customers receive their orders in a timely manner, even if the product is temporarily out of stock.
In conclusion, supply chain analytics is of utmost importance in the modern business world. It provides a clarification on the meaning and interpretation of data points related to the supply chain, helping organizations optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and make data-driven decisions. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding and improving backorder situations, which play a crucial role in the overall performance of a supply chain.
Automated Reorder Systems
In the understanding and meaning of backordered items, it is important to point out the importance of automated reorder systems. These systems play a significant role in the clarification and interpretation of backorders. The purpose of automated reorder systems is to prevent the occurrence of backordering by ensuring that inventory levels are constantly monitored and reorder points are established.
An automated reorder system works by tracking the sales and inventory levels of products. When the inventory of a particular item reaches a predefined reorder point, the system automatically generates an order to replenish that item. This proactive approach helps to avoid the backorder situation and ensures that products are always available for customers.
One of the reasons why automated reorder systems are of great importance is their ability to save time and effort. With these systems in place, businesses no longer need to manually monitor inventory levels and manually create purchase orders. This automation not only improves efficiency but also reduces the chances of human error in the ordering process.
Furthermore, automated reorder systems contribute to the definition and sense of backordering. By preventing the occurrence of backorders, businesses can avoid the negative consequences that come with delayed deliveries and dissatisfied customers. This explanation of backordering goes beyond the surface level and dives into the logistical aspects of supply chain management.
In summary, automated reorder systems play a crucial role in the understanding and interpretation of backorders. Their significance lies in their ability to prevent backordering, save time and effort, and improve overall customer satisfaction. Businesses that utilize these systems can ensure smooth operations and minimize the occurrence of backordered items.