The specific identification method is a valuation system used in accounting to track the cost of individual items in inventory. This method is particularly important for businesses that deal with high-value or unique items, such as art galleries or luxury goods retailers. By using the specific identification method, businesses can accurately track the cost of each item and determine the value of their inventory.
Unlike other inventory valuation methods, such as the FIFO (first-in, first-out) or average cost methods, the specific identification method allows businesses to assign the exact cost of each item to its sale or usage. This is especially important when dealing with items that have different costs, such as antique furniture or high-end electronics.
With the specific identification method, businesses can track the movement of specific units of goods within their inventory. This means that if an item is sold, the cost of that specific item is deducted from the inventory and recorded on the income statement. This level of detail provides a more accurate picture of the cost of goods sold and allows for better decision-making.
The specific identification method is particularly useful for businesses that deal with items that have varying costs, such as perishable goods or items with unique serial numbers. By accurately tracking the cost and movement of these individual items, businesses can ensure that their financial statements reflect the true value of their inventory and make informed decisions regarding pricing, restocking, and profitability.
In conclusion, the specific identification method is an important accounting tool that allows businesses to accurately track the cost of individual items in their inventory. This method provides a more accurate valuation of goods and enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding their inventory management and financial performance. By utilizing the specific identification method, businesses can improve their cost tracking system and ensure the integrity of their accounting records.
What is the Specific Identification Method?
The Specific Identification Method is a tracking method used in accounting to assign costs to individual units of inventory. Unlike average or weighted methods, which assign the same cost to all units of a particular item, the specific identification method allows for the unique identification and valuation of each individual item.
Under this method, a company maintains detailed records for each item in its inventory, including the cost at which it was acquired or produced. When inventory is sold, the company can accurately determine the cost of goods sold by matching the specific cost of each sold unit with the corresponding revenue earned from the sale.
The specific identification method is particularly useful when dealing with inventory that has distinct characteristics or unique costs. For example, if a company sells jewelry with different gemstone arrangements, each piece may have a different cost based on the specific gemstones used. By using the specific identification method, the company can accurately track the cost of each individual piece and determine the overall profit or loss on each sale.
It's important to note that while the specific identification method provides a more accurate representation of inventory costs, it may be more complex and time-consuming to implement compared to alternative methods like the first-in, first-out (FIFO) or weighted average methods.
In conclusion, the specific identification method is a valuable tool in accounting for accurately tracking and valuing inventory. It allows for the recognition of unique costs associated with each individual item, providing a more precise reflection of the company's financial position. This method is particularly helpful for businesses that deal with inventory items that have distinct characteristics or vary significantly in cost.
Definition and Explanation
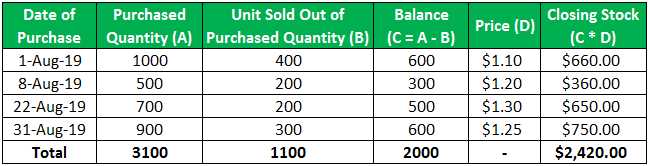
The specific identification method is a weighted inventory valuation method used in accounting. It involves tracking and recording the individual costs of items in inventory. This method is different from other methods such as FIFO (first-in, first-out) or average cost, where costs are allocated based on the average cost of the goods.
With the specific identification method, each item in inventory is assigned a specific cost, making it easier to track and value individual units. This method is especially useful when dealing with unique or high-value items, as it allows for more accurate accounting of the actual costs associated with each particular item.
Specific identification method is particularly important in industries where inventory turnover is high and goods have varying costs. By accurately identifying and valuing each item, businesses can have a better understanding of their inventory costs and make more informed decisions about pricing, purchasing, and profitability.
This method requires meticulous record-keeping, as each item must be identified and its associated cost recorded. However, the benefit of accurate tracking and valuation outweighs the additional administrative efforts. By utilizing the specific identification method, businesses can enhance their financial reporting and gain insights into their inventory management practices.
In conclusion, the specific identification method is an accounting technique that assigns specific costs to each item in inventory, allowing for accurate tracking and valuation of goods. This method is particularly valuable in industries with unique or high-value items and helps businesses make informed decisions regarding pricing, purchasing, and profitability.
How Does it Work?
The specific identification method is an accounting system that tracks the costs of individual items in inventory. Unlike other cost allocation methods, such as the weighted average or first-in, first-out (FIFO), the specific identification method allows for the precise valuation of each item in inventory.
Under the specific identification method, each item in inventory is assigned a unique identification number or code, allowing it to be easily tracked in the accounting records. This method is especially useful for industries where items have distinct characteristics or attributes that affect their value, such as high-end retail or specialized manufacturing.
By using the specific identification method, companies can more accurately determine the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the value of their ending inventory. For example, if a company sells three units of a particular item in a given period, the specific identification method allows for the identification of the exact cost associated with those three units.
This detailed analysis of costs is crucial for accurate financial reporting, as it provides a more precise picture of a company's profitability and inventory valuation. The specific identification method ensures that each item is accounted for individually, preventing distortions in pricing and cost allocation that can occur with other methods.
In summary, the specific identification method in accounting is a detailed system for tracking the costs of individual items in inventory. By assigning unique identification numbers or codes to each item, companies can accurately determine the cost of goods sold and the value of their ending inventory. This method allows for precise valuation and prevents distortions in pricing and cost allocation.
Importance of the Specific Identification Method
The specific identification method is an important accounting approach that allows businesses to assign the cost of each individual item in their inventory. This method is particularly useful when the items being tracked vary significantly in cost.
By using the specific identification method, businesses can more accurately determine the cost of goods sold and the value of their ending inventory. This is especially beneficial for businesses that deal with high-value or unique items, such as luxury goods or customized products.
Unlike other cost allocation methods like the average cost or FIFO (first-in, first-out), the specific identification method provides a more precise valuation of inventory. It enables businesses to identify the exact cost associated with each unit sold or remaining in inventory. This level of detail is crucial for making informed financial decisions and meeting reporting requirements.
Using the specific identification method also enables businesses to track the cost of specific items throughout their lifecycle. This information can be valuable in determining pricing strategies, evaluating the profitability of specific product lines, and identifying any potential issues with inventory management.
In addition to financial benefits, the specific identification method can also be helpful in complying with regulatory requirements. In industries where strict regulations govern inventory valuation and reporting, utilizing this method ensures accurate and transparent records.
In summary, the specific identification method is an important tool in accounting that provides businesses with a more precise valuation of their inventory. It allows for tracking individual item costs, making informed financial decisions, and meeting reporting requirements. This method is particularly useful for businesses dealing with high-value or unique items.
Accurate Cost Reporting
In accounting, accurate cost reporting is essential for proper financial management and decision-making. One method that helps achieve accurate cost reporting is the specific identification method, which tracks the cost of individual units or items in the inventory.
Unlike the weighted average method, where the cost of goods is determined based on the average cost of all inventory units, the specific identification method assigns the actual cost of each item in the inventory. This method is particularly useful for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items, where each unit has a distinct cost.
The specific identification method ensures that the valuation of inventory accurately reflects the cost of the goods. By keeping detailed records of the cost of each item, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing, profitability, and inventory management.
Implementing the specific identification method requires careful tracking of costs for each individual item. This can be done through the use of barcodes, serial numbers, or other identification systems. Additionally, it is crucial to maintain accurate records that clearly document the cost of each item and its subsequent sale or disposal.
Compared to other cost tracking methods like FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or weighted average, the specific identification method provides a more precise and detailed picture of the inventory cost. This level of accuracy is especially important for businesses operating in industries with volatile costs or when dealing with unique or custom-made goods.
In conclusion, accurate cost reporting is essential for effective accounting and financial management. The specific identification method offers a detailed and accurate approach to tracking and valuing inventory costs. By implementing this method and maintaining meticulous records, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize profitability and inventory management.
Proper Income Calculation
When it comes to calculating the income generated by a business, it is crucial to have accurate and reliable methods. One of the most important factors in proper income calculation is the accurate tracking and valuation of inventory. It is essential for businesses to keep detailed records of the items they have in stock, their individual costs, and the specific identification method used to value and allocate these costs.
The specific identification method allows businesses to track and allocate costs to specific units or items in their inventory. This method is especially useful when dealing with unique or high-value items, where each item has a different cost. By utilizing this method, businesses can accurately determine the cost of goods sold and the value of their remaining inventory.
In addition to the specific identification method, there are other common methods used in accounting for inventory valuation. One such method is the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method, which assumes that the first items purchased are the first to be sold. Another method is the weighted average method, which calculates the average cost of the units in inventory.
Proper income calculation relies on choosing the most appropriate method for tracking and valuing inventory. This ensures that businesses can accurately determine their cost of goods sold, gross profit, and overall income. It is important for businesses to establish effective record-keeping systems and employ trained professionals to handle the accounting and valuation of inventory items.
Having accurate and reliable records is not only important for internal reporting and decision-making but also for external stakeholders such as investors, lenders, and tax authorities. They rely on the financial statements provided by the business to make informed decisions and assess the financial health of the company.
Application of the Specific Identification Method
The specific identification method is an accounting system that allows businesses to track and assign costs to individual items in their inventory. This method is commonly used when dealing with unique or high-value items, where it is important to accurately determine the cost of each individual unit.
Under this method, each item in the inventory is assigned a specific identifying number or code, which is then used to track its cost. This allows businesses to keep detailed records of the cost of each item, as well as any associated expenses such as transportation or storage.
By using the specific identification method, businesses can accurately determine the cost of goods sold and the value of their remaining inventory. This is especially important for businesses that deal with items that have varying costs, such as precious metals or custom-made products.
Compared to other inventory tracking methods, such as the average or weighted methods, the specific identification method provides a more precise calculation of costs. This is because it takes into account the actual cost of each individual item, rather than relying on averaged or weighted costs.
One common alternative to the specific identification method is the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, which assumes that the first items purchased are the first ones sold. While FIFO is widely used in accounting, it may not be suitable for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items, as it does not account for the individual costs of each item.
In conclusion, the specific identification method is a valuable tool in accounting for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items. By tracking and assigning costs to individual items, businesses can accurately determine the value of their inventory and make informed financial decisions.
Industries that Benefit from Specific Identification
The specific identification method is a valuable tool in accounting, particularly for industries that deal with individual and unique items in their inventory. This method allows businesses to track the cost and valuation of each unit or item separately, providing a more accurate reflection of the inventory's value.
One industry that greatly benefits from the specific identification method is the jewelry industry. Jewelers often have a wide variety of unique and high-value items in their inventory, each with its own cost and market value. By using specific identification, jewelers can track the cost of each individual item and adjust the valuation accordingly. This allows for better decision-making when it comes to pricing, restocking, and managing the inventory.
The automotive industry is another sector that benefits from the specific identification method. Dealerships and manufacturers often have different models and options, each with varying costs and pricing. By using specific identification, they can accurately track the cost of each vehicle and determine its profitability. This information is crucial for managing inventory levels, negotiating with suppliers, and setting competitive prices.
The pharmaceutical industry is also highly dependent on the specific identification method. Drug manufacturers and distributors deal with different types of medicines with varying costs and expiration dates. By using specific identification, they can ensure that the oldest and most expensive items are sold first, reducing the risk of expired inventory and minimizing costs. This method also allows for accurate tracking of product recalls or quality issues.
In addition to these industries, any business that deals with unique or high-value items can benefit from the specific identification method. This includes art galleries, antique stores, specialty retailers, and more. By accurately tracking the costs and valuations of individual items, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing, promotions, and inventory management.
Jewelry and Gemstones
Jewelry and gemstones are valuable items that require careful records and tracking in accounting systems. The specific identification method is often used to accurately account for the cost and units of these unique items. This method allows businesses to assign individual costs to each inventory item, which is especially important for jewelry and gemstones due to their varying values.
Using the specific identification method, businesses can track the cost of each individual jewelry piece or gemstone, allowing for more accurate inventory valuation. This method is particularly useful when items have different costs, such as when dealing with unique gemstones of varying quality or rare and one-of-a-kind jewelry pieces.
Compared to other inventory valuation methods like FIFO (first in, first out) or average cost, the specific identification method provides a more precise way of accounting for the value of goods. It eliminates the need to assign an average cost to items or make assumptions about which items are sold first, ensuring that the inventory is accurately valued.
In the case of jewelry and gemstones, where each item can have significantly different values, the specific identification method is crucial for accurate accounting and tracking. By recording the individual cost of each jewelry piece or gemstone, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, inventory management, and financial reporting.
Overall, the specific identification method is an essential tool in the accounting system for businesses dealing with jewelry and gemstones. It allows for precise tracking of costs and units, ensuring accurate inventory valuation and financial reporting.
Art and Collectibles
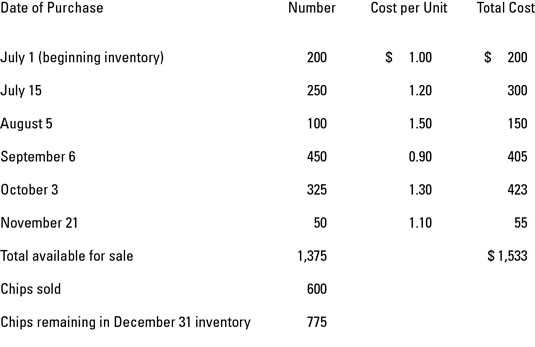
When it comes to accounting for art and collectibles, specific identification becomes even more crucial. These unique items require accurate records of their identification, costs, and methods of valuation. The specific identification method allows businesses to track each individual item and assign a specific cost to it.
One commonly used method for valuing art and collectibles is the FIFO (first-in, first-out) method. This means that the oldest items in the inventory are assumed to be sold first. Using this method, the costs associated with the oldest items are used to value the goods sold. The weighted average method is another common approach. It calculates the average cost of all the units available for sale and uses this average cost to value the goods sold.
Accounting for art and collectibles also requires careful tracking of inventory. An inventory tracking system should be in place to keep a record of each item, its acquisition cost, and any subsequent changes in value. This allows for accurate valuation of the items for financial reporting purposes.
Given the unique nature of art and collectibles, it is important for businesses to use a specific identification method. This method ensures that the costs associated with each individual item are accurately reflected in the accounting records. It allows for a more precise valuation of assets and can help businesses make informed decisions regarding their art and collectibles.
In conclusion, applying specific identification methods in accounting for art and collectibles is crucial. It enables accurate tracking of individual items, determines their costs, and provides a more precise valuation for financial reporting purposes. Understanding these methods is essential for ensuring proper accounting of these unique and valuable assets.
Aerospace and Defense
Valuation: Aerospace and defense companies rely on accurate valuation of their inventory due to the high value and complexity of their products. Valuation methods such as weighted average cost, specific identification, and FIFO (first-in, first-out) are commonly used to determine the cost of goods.
Records: Keeping detailed and accurate records is crucial for aerospace and defense companies. They need to track the costs of individual items in their inventory, including the specific identification of each unit. This level of record-keeping ensures transparency and helps with thorough financial reporting.
Inventory methods: Aerospace and defense companies often employ sophisticated inventory tracking systems to manage their large and diverse inventories. These systems enable them to efficiently track and manage thousands of different items and their associated costs.
Cost tracking: With the specific identification method, aerospace and defense companies can track the cost of individual items in their inventory. This allows for a more accurate picture of the company's financial health and helps with decision-making regarding pricing, production, and inventory management.
Importance in accounting: The specific identification method is especially important in the aerospace and defense industry due to the unique characteristics of their products. From aircraft parts to advanced defense systems, each item can have a significantly different cost and value. Using specific identification ensures that the most accurate cost is assigned to each item, providing a more accurate reflection of the company's financial position.
Challenges and Limitations of Specific Identification
Tracking: One of the challenges of using the specific identification method is the difficulty in tracking individual items and their costs. This method requires keeping detailed records for each specific item in inventory, including its purchase price and other associated costs. It can be time-consuming and complex to continuously update these records as new items are purchased or sold.
Multiple Methods: Another limitation of specific identification is that it may not be feasible when a large number of similar items are in inventory. In such cases, alternative cost allocation methods, such as the average cost method or the weighted average method, may be more practical. These methods calculate the cost of goods sold and the value of ending inventory based on an average cost per unit.
Valuation: Specific identification may also present challenges in accurately valuing inventory. If the specific costs of goods cannot be determined, or if a specific item is sold but its cost cannot be identified, it can be difficult to accurately determine the value of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold. This can impact the accuracy of financial statements and affect decision-making processes.
Complexity: The specific identification method can be complex to implement and maintain, especially for companies with large inventories or frequent inventory turnover. It requires a robust inventory management system and well-organized records to properly track and identify specific items and their costs. This complexity can increase the risk of errors or discrepancies in accounting records, which can have a significant impact on financial reporting.
Subjectivity: Another limitation of specific identification is that it involves a certain level of subjectivity. The decision of which specific items to identify and allocate costs to can be influenced by personal judgment or bias. This subjectivity presents a risk of manipulation or misrepresentation of financial information, especially if there are incentives to overstate or understate inventory values.
Overall, while the specific identification method offers advantages in terms of accuracy and matching specific costs to individual items, it also presents challenges and limitations in terms of tracking, valuation, complexity, and subjectivity. Companies must carefully consider these factors and assess the suitability of this method for their specific inventory management needs and operational circumstances.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a crucial aspect of running a successful business. It involves tracking and controlling the flow of goods or items in and out of a company's inventory. There are various methods and systems that can be used to manage inventory, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
One popular method used in inventory management is the average cost method. This method calculates the value of the inventory by taking the average cost of all the goods or items in stock. This provides a more accurate valuation of the inventory, as it takes into account variations in the cost of goods.
Another commonly used method is the specific identification method. Under this method, each individual item in the inventory is tracked and recorded separately, along with its specific cost. This allows for a more precise valuation of the inventory, as it takes into account the actual cost of each item.
The FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method is another widely used method in inventory management. This method assumes that the first items purchased are the first ones sold. It values the inventory using the cost of the oldest items in stock, which can be helpful in industries where the cost of goods tends to rise over time.
Inventory management systems are essential tools for businesses as they provide a means for effective tracking and control of inventory. These systems enable businesses to maintain accurate records of inventory levels, costs, and valuations, allowing for informed decision-making and efficient use of resources.
Overall, effective inventory management is vital for businesses to ensure smooth operations and maximize profitability. By implementing appropriate tracking methods and systems, businesses can optimize their inventory management processes, minimize costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Record-Keeping Complexity
One of the biggest challenges in accounting is the complexity of record-keeping. With the myriad of methods available for tracking goods and items, it can be difficult to maintain accurate inventory records. One method that can help simplify this process is the specific identification method.
Under the specific identification method, each individual item in inventory is tracked separately. This means that each item is assigned a specific identification number or code, and its cost is recorded as it is purchased or sold. By keeping records of the specific costs for each item, companies can easily determine the value of their inventory at any given time.
Unlike other valuation methods, such as the weighted average or First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method, the specific identification method allows for a more precise cost allocation. This is particularly useful for companies that deal with high-value or unique items, as it allows them to accurately account for the cost of each individual unit.
However, the specific identification method also adds an extra layer of complexity to the accounting system. Companies must ensure that each item has a unique identification number or code, and they must carefully track the cost of each item as it moves through the inventory. This requires detailed record-keeping and diligent tracking of purchase and sale transactions.
In conclusion, while the specific identification method provides a more precise cost allocation and valuation of inventory, it also adds complexity to the record-keeping process. Companies must carefully implement and maintain a system to track individual items and their costs. By doing so, they can ensure accurate and reliable financial statements.
Comparison with Other Inventory Valuation Methods
In accounting, there are several methods used to determine the value of inventory items. One of these methods is the specific identification method. This method differs from other inventory valuation methods such as FIFO (first-in, first-out) and weighted average cost.
The specific identification method involves tracking the actual cost of each individual item in inventory. This method is commonly used for items that have a unique identification number or serial number. By using this method, a company can accurately determine the cost of each individual item in its inventory.
On the other hand, FIFO and weighted average cost methods do not track the actual cost of each individual item. FIFO assumes that the first goods purchased are the first goods sold, while the weighted average cost method calculates the average cost of all units in inventory.
Compared to FIFO and weighted average cost methods, the specific identification method provides more accurate inventory valuations. This method ensures that each item is valued at its specific cost, rather than an average cost or an assumed order of acquisition. Therefore, companies that deal with high-value items or unique inventory items may prefer to use the specific identification method to maintain accurate records of their inventory costs.
- Advantages of the specific identification method:
- Accurate valuation of individual inventory items
- Precise tracking of inventory costs
- Ability to identify specific costs for specific items
- Disadvantages of the specific identification method:
- Requires detailed record keeping for each item
- May not be practical for companies with large inventories
In conclusion, the specific identification method offers a more precise approach to valuing inventory items compared to other methods such as FIFO and weighted average cost. Although it requires more detailed record keeping, this method is essential for accurately tracking and attributing costs to individual goods in a company's inventory.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Method
The First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method is a common inventory valuation method used in accounting. This method assumes that the first items purchased or produced are the first items sold or used, thus the name "first-in, first-out".
FIFO method relies on the individual tracking and valuation of each item or unit in inventory. Under this method, each item is assigned a specific cost based on its purchase or production date. When calculating the cost of goods sold or inventory value, the oldest items (first-in) are used first.
This method is important because it helps businesses in accurately tracking the cost of goods sold and the value of inventory. By keeping records of the purchase or production date and cost of each item, FIFO method ensures accurate valuation of the inventory. It also allows for better cost control and informed decision-making.
Under FIFO method, the cost of sold goods is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the weighted average cost of the oldest items. This helps in reflecting the actual cost incurred to produce or purchase the goods that were sold.
Overall, FIFO method is widely used in businesses as it provides a clear and transparent system for tracking inventory costs. It is particularly useful when dealing with inventory items that have different costs over time. By following the first-in, first-out principle, businesses can accurately reflect the cost of goods sold and make informed financial decisions.
Definition and Explanation
The specific identification method is a valuation method used in accounting to track the costs of individual items within a company's inventory. Unlike the average cost method or the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, which calculate the average or oldest costs of similar goods, the specific identification method allows for the tracking of costs associated with each individual item in inventory.
Under the specific identification method, a company maintains detailed records of the cost of each item in its inventory, allowing for precise valuation. This method is particularly useful for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items, such as artwork, jewelry, or specialized equipment.
This method involves tracking the specific cost of each item from the time it was acquired to the time it is sold. By recording the exact costs associated with each individual item, a company can accurately calculate its cost of goods sold and determine the profitability of each sale.
One advantage of the specific identification method is that it provides a more accurate representation of the company's inventory value and profitability. It allows for the recognition of the actual costs associated with individual units, which can result in more precise financial statements and tax calculations.
However, the specific identification method can be more time-consuming and complex than other valuation methods, as it requires detailed record-keeping and tracking of each item's costs. Additionally, the method may not be feasible for businesses with a large number of low-value items or those with limited resources for record-keeping.
In conclusion, the specific identification method is a valuable tool in accounting for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items. While it may require more effort and resources to implement, this method provides a more accurate reflection of inventory valuation and can offer insights into the profitability of individual sales.
Differences from Specific Identification
When it comes to accounting for inventory, there are various methods that can be used. While the specific identification method involves tracking the cost of each individual item, there are other methods, such as the average cost method and the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method, which rely on different techniques to determine the cost of goods sold and the value of the remaining inventory.
The average cost method calculates the cost of inventory by taking the average cost of all units in stock. This is done by dividing the total cost of inventory by the total number of units. This method creates a more generalized valuation of inventory, as it considers all units as having equal cost.
The FIFO method, on the other hand, assumes that the first items purchased or produced are the first to be sold. As a result, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest units in stock, while the ending inventory is valued using the cost of the most recent units. This method is often used when the cost of inventory is increasing over time, as it results in a higher ending inventory value and a lower cost of goods sold.
Compared to the specific identification method, both the average cost method and the FIFO method provide a more generalized approach to inventory valuation. The specific identification method, on the other hand, allows for the precise tracking of the cost of each individual item in inventory. This can be particularly useful for companies that deal with unique or high-value items, as it allows for a more accurate recording of costs and potential profits. However, this method requires meticulous records and can be more time-consuming than other methods.
In conclusion, while each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, the specific identification method stands out as the most precise and detailed approach to inventory accounting. However, it may not be suitable for all businesses and may require additional resources for accurate record-keeping. Ultimately, the choice of inventory valuation method will depend on the specific needs and circumstances of each individual company.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) Method
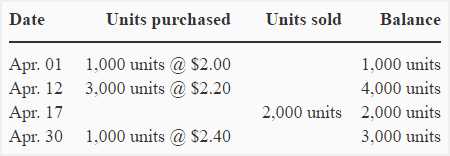
The Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) method is an inventory valuation method used in accounting. It assumes that the last units received or produced are the first units to be sold or used. This means that when calculating the cost of goods sold, the costs of the most recently acquired or produced items are used.
Under the LIFO method, individual items in the inventory are not specifically identified. Instead, the system tracks the total number of units and their associated costs. When goods are sold or used, the cost of the most recent units is matched to the revenue generated.
The LIFO method can be particularly useful in certain situations. For example, when inventory costs are increasing over time, using the LIFO method can result in a lower cost of goods sold, which can lead to lower taxable income and, therefore, lower taxes. Additionally, the LIFO method can reflect a more accurate valuation of inventory costs in industries where an item's cost fluctuates significantly.
One of the drawbacks of the LIFO method is that it can result in outdated inventory records. This is because the cost of the oldest units in the inventory is not reflected in the calculation of the cost of goods sold. As a result, the inventory on the balance sheet may be valued at outdated costs, which can affect the accuracy of financial statements.
Compared to other inventory valuation methods, such as the specific identification method, weighted average cost method, and First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method, the LIFO method may not reflect the actual flow of goods through a business. However, it can be a valuable tool in certain circumstances for managing costs and taxation.
Definition and Explanation
The specific identification method is an inventory tracking method in accounting that assigns costs to individual items based on their actual purchase or production costs. This method allows businesses to accurately track the valuation of their inventory by attributing specific costs to each item sold or remaining in stock.
Under the specific identification method, the costs of goods sold and ending inventory are determined by identifying and tracking the cost of each individual item sold or remaining in inventory. This is in contrast to other methods such as weighted average or FIFO (First-In, First-Out), which use average or predetermined costs for groups of similar items.
The specific identification method is particularly useful for businesses that deal with unique or high-value items, as it provides a more accurate representation of their inventory valuation. By individually identifying the cost of each item, businesses can better manage their inventory and make informed pricing decisions to optimize their profitability.
In order to use the specific identification method, businesses need to have a system in place that allows them to track each item from purchase or production through to sale. This can be done through the use of unique identifiers, such as serial or batch numbers, or through meticulous record-keeping.
Overall, the specific identification method is an important tool in accounting as it provides businesses with a more precise and detailed understanding of their inventory costs. By using this method, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting and make more informed decisions regarding their inventory management and pricing strategies.
Differences from Specific Identification
While the specific identification method in accounting allows for the individual tracking and valuation of each item or unit in a company's inventory, there are several alternative methods that can be employed when specific identification is not feasible or practical.
One commonly used alternative is the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method. With FIFO, the cost of goods sold is calculated based on the assumption that the oldest units in inventory are sold first. This method can be useful for companies that deal with perishable goods or goods that have a short shelf life.
Another method is the weighted average cost method. This method determines the cost of goods sold by calculating the average cost of all units in inventory, regardless of when they were acquired. It takes into account the quantity and cost of each item in inventory to determine the average cost per unit.
Unlike specific identification, which requires a more detailed record-keeping system, both the FIFO and weighted average cost methods rely on a less granular approach to tracking and valuing inventory. These methods provide a more streamlined way to calculate the cost of goods sold, but they may not provide as accurate a picture of individual item costs as the specific identification method.
In conclusion, while the specific identification method in accounting offers the most precise and detailed tracking of inventory costs, alternative methods such as FIFO and the weighted average cost method provide more simplified approaches to valuing goods. Companies must choose the method that best suits their needs and the nature of their inventory.