In the field of accounting, fringe benefits are a crucial component of an employee's total compensation. Fringe benefits are additional forms of compensation provided by employers to their employees, apart from their regular wages or salary. These benefits can include various insurance plans, such as health, dental, and vision insurance, as well as retirement plans and paid time off.
One of the main advantages of fringe benefits is that they provide a safety net for employees in case of unexpected events, such as illness or injury. Insurance plans included in fringe benefits can help employees cover medical expenses and ensure their well-being. Furthermore, fringe benefits also contribute to attracting and retaining talented individuals, as they enhance job satisfaction and work-life balance.
Employers offer fringe benefits as a way to incentivize and motivate employees, recognizing their contributions to the organization. These benefits can range from flexible work schedules and access to gym memberships to transportation assistance and childcare subsidies. By providing such perks, employers aim to promote employee loyalty and productivity.
From an accounting perspective, fringe benefits are considered part of an employee's compensation package and are subject to certain tax regulations. Employers are required to report the value of fringe benefits provided to employees on their annual payroll tax returns. Additionally, employees may have to pay taxes on the value of these benefits, depending on the specific regulations in their country or region.
Understanding Fringe Benefits in Accounting

In the realm of accounting, fringe benefits play a crucial role in determining an employee's compensation. Fringe benefits refer to the additional perks and advantages that employers offer to their employees, apart from their regular salary. These benefits are designed to provide employees with extra financial security and incentives, ensuring their well-being and job satisfaction.
One key aspect of fringe benefits is their tax treatment. While regular salary is subject to income taxes, certain fringe benefits are often taxed at a different rate or may even be tax-exempt. Understanding the tax implications of different fringe benefits is essential for accurate accounting and payroll calculations.
Expenses related to fringe benefits can significantly impact an organization's financial statements. In accounting, it is crucial to properly allocate and track these expenses to ensure the accuracy of financial reports. This includes recording the cost of providing fringe benefits, such as health insurance or retirement plans, as well as any employer contributions made towards these benefits.
From an employee's perspective, fringe benefits can greatly enhance their overall compensation package. These benefits can include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, employee discounts, and more. Understanding and properly valuing these benefits is essential for determining an employee's total compensation and ensuring fairness in the workplace.
Accounting for fringe benefits also involves deducting the cost of these benefits from an employee's gross pay to determine their taxable wages. This deduction reduces the amount of income subject to taxes, resulting in potential tax savings for both the employee and the employer.
Overall, understanding fringe benefits in accounting is crucial for accurately valuing an employee's total compensation package, managing costs, and complying with tax regulations. By carefully accounting for these benefits, organizations can ensure fair and transparent practices when it comes to employee compensation.
What Are Fringe Benefits?
Fringe benefits are additional perks or benefits that are provided to employees on top of their regular salary. These benefits are often offered as a part of a compensation package and can include a variety of different options such as insurance, retirement plans, vacation time, and more.
One common way employers provide fringe benefits is through offering health insurance plans. This can help employees cover medical expenses and can be a valuable tool in attracting and retaining top talent. Other common fringe benefits include retirement plans, such as 401(k) plans, which allow employees to save for their future.
In addition to insurance and retirement plans, fringe benefits can also include paid vacation time, flexible work schedules, and bonuses. These benefits can help improve employee satisfaction and morale, and can also serve as incentives for employees to work harder and stay with a company for a longer period of time.
From an accounting perspective, fringe benefits are an important consideration when calculating an employee's total compensation. These benefits need to be accounted for in a company's payroll and financial statements. The value of fringe benefits is typically included in an employee's gross pay and is subject to various deductions and withholding for taxes.
Overall, fringe benefits are an important aspect of an employee's total compensation and can have a significant impact on their job satisfaction and financial well-being. Employers need to carefully consider the benefits they offer in order to attract and retain talented employees, while also managing the costs and expenses associated with providing these benefits.
Importance of Fringe Benefits in Accounting
In accounting, fringe benefits play a crucial role in managing the financial aspects of an employee's compensation. These benefits, also known as employee perks or fringe benefits, go beyond just wages and provide valuable incentives to enhance the overall compensation package.
One of the key reasons why fringe benefits are important in accounting is because they form an integral part of an employee's total compensation. While wages represent the basic pay for the work done, fringe benefits add additional value to the overall package. Accounting for these benefits ensures that the employee's total compensation is accurately reflected in the payroll records.
Furthermore, accounting for fringe benefits helps in accurately calculating the employee's net pay and withholding the appropriate taxes. By including these benefits in the payroll calculations, the employee's income tax deductions can be appropriately adjusted, ensuring that the correct amount of taxes are withheld.
In addition, fringe benefits often include various types of insurance coverage, such as health insurance or life insurance. By accounting for these benefits, the employer can accurately track the expenses related to insurance coverage and ensure that the appropriate tax deductions are applied.
Moreover, fringe benefits are an important aspect of attracting and retaining talented employees. Offering attractive perks and benefits can help a company stand out in the job market and create a competitive advantage. By accounting for these benefits, the company can accurately assess the cost of providing these perks and gauge their impact on employee satisfaction and retention.
In conclusion, accounting for fringe benefits is essential in managing the financial aspects of an employee's compensation. It ensures accurate calculation of net pay, appropriate tax withholding, and tracking of expenses related to benefits such as insurance. Additionally, accounting for these benefits allows companies to evaluate the impact of perks on employee satisfaction and retention, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Tax Implications of Fringe Benefits
When it comes to wages and benefits, fringe benefits are a type of compensation that an employee receives in addition to their regular salary or wages. These fringe benefits can include various non-monetary perks, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and company car allowances, among others.
From a payroll and tax perspective, it is important to understand the tax implications of these fringe benefits. First and foremost, the value of these benefits is generally considered taxable income for the employee. This means that they must be included in the employee's gross pay for tax purposes, and taxes must be withheld accordingly.
Employers are responsible for properly accounting for these fringe benefits and ensuring that the appropriate taxes are withheld and reported to tax authorities. Failure to do so can result in penalties and legal consequences. Therefore, it is crucial for employers to have accurate and up-to-date records of the fringe benefits provided to each employee.
In addition to income taxes, there may also be other tax implications associated with providing fringe benefits. For example, some fringe benefits may be subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as federal and state unemployment taxes. Employers should be aware of these potential tax obligations and comply with the relevant tax laws and regulations.
Overall, while fringe benefits can be a valuable component of an employee's compensation package, it is essential for both employers and employees to understand and comply with the tax implications associated with these benefits. This requires careful accounting and withholding practices to ensure accurate reporting and payment of the necessary taxes.
Types of Fringe Benefits
There are various types of fringe benefits that employers may offer to their employees as a part of their compensation package. These benefits go beyond the basic salary and can include a range of perks and incentives. Some of the common types of fringe benefits are:
- Health Insurance: Employers may provide health insurance plans to their employees, covering the cost of medical expenses and ensuring access to quality healthcare.
- Retirement Plans: Employers may offer retirement benefit plans such as a 401(k) or pension plans, allowing employees to save for their future and enjoy financial security after retirement.
- Vacation and Paid Time Off: Employers may provide paid vacation days, personal days, or sick leave to employees, allowing them to take time off from work without sacrificing their income.
- Flexible Spending Accounts: These accounts allow employees to set aside a portion of their pre-tax salary to pay for qualified medical, childcare, or transportation expenses.
- Education Assistance: Some employers offer tuition reimbursement or assistance programs, allowing employees to pursue higher education or gain additional job-related skills.
- Transportation Benefits: Employers may provide transportation benefits, such as subsidized commuting costs or parking allowances, to help employees offset their commuting expenses.
- Life Insurance: Employers may offer life insurance coverage as a fringe benefit, providing financial protection to employees' beneficiaries in the event of their death.
These fringe benefits are an essential part of an employee's compensation package and are often subject to various deductions and withholding for taxes and accounting purposes. They can significantly enhance an employee's overall income and job satisfaction, making them a valuable tool for attracting and retaining top talent.
Health Insurance
Health insurance is an important employee benefit that provides coverage for medical expenses. It is considered a fringe benefit, which is a non-monetary form of compensation provided by employers to attract and retain employees.
Employers often offer health insurance as part of a comprehensive benefits package to incentivize employees to stay with the company and to help them manage the costs of medical care.
Health insurance premiums are typically deducted from an employee's wages or salary, and the employer may also contribute towards the cost. These deductions are usually made on a pre-tax basis, which means that the amount of the premium is subtracted from the employee's gross pay before taxes are withheld. This can result in tax savings for the employee.
In addition to health insurance premiums, employees may also have other healthcare-related expenses that are eligible for deductions. For example, out-of-pocket expenses such as copayments, deductibles, and prescription medications can be deducted from an employee's income.
From an accounting standpoint, health insurance expenses are recorded as part of the company's payroll and benefits costs. This includes not only the cost of the premiums but also any contributions made by the employer towards the coverage. These expenses are typically classified as operating expenses on the company's income statement.
Overall, health insurance is an important component of an employee's compensation package, providing financial protection and peace of mind when it comes to managing healthcare expenses. It also has implications for accounting and tax purposes, as employers must track and report these expenses accurately.
Retirement Plans
In the world of accounting and payroll, retirement plans play a crucial role in an employee's overall compensation package. Retirement plans are designed to help employees save for their future and provide them with a source of income during their retirement years.
Retirement plans are considered a fringe benefit and are often offered by employers as part of an employee's total compensation package. These plans are typically funded by a combination of employer and employee contributions.
There are various types of retirement plans available, such as 401(k) and 403(b) plans. These plans allow employees to contribute a portion of their salary, on a pre-tax basis, towards their retirement savings. Employers often match a percentage of the employee's contribution, providing them with an additional incentive to save for retirement.
One of the main advantages of participating in a retirement plan is the ability to defer taxes on the income and investment gains until the funds are withdrawn during retirement. This can result in significant tax savings and allow employees to maximize their retirement savings.
Additionally, retirement plans may offer other perks such as employer-provided insurance and other benefits. These benefits can further enhance an employee's overall compensation package and provide them with extra security and peace of mind.
In summary, retirement plans are an important component of an employee's overall compensation and can provide them with a reliable source of income during their retirement years. By participating in a retirement plan, employees can maximize their savings, take advantage of tax benefits, and secure their financial future.
Paid Time Off (PTO)
Paid Time Off (PTO) refers to the time that an employee is compensated for when they are not working. This can include vacation time, personal days, and sick leave. PTO is typically accrued based on the amount of time an employee has worked for a company and is often included as part of their overall compensation package.
PTO can be considered a fringe benefit, as it is an additional perk provided by the employer on top of an employee's salary or wages. It is an important component of employee benefits and can be a significant cost for companies to manage and administer.
From an accounting perspective, PTO is considered a liability, as it represents a future expense that the company will need to pay out to employees. Companies must track and record PTO accruals and usage, as well as any payouts or carryover amounts. These calculations are usually done as part of the company's payroll process.
In addition to the financial implications, PTO can also have an impact on an employee's taxes and withholdings. The value of PTO is typically included in an employee's gross pay, and taxes and other deductions are calculated based on this amount. This means that PTO can affect the employee's overall income and tax obligations.
Employers may offer different types of PTO policies and may also provide incentives for employees to use their PTO. For example, some companies may offer paid leave for volunteering or allow employees to cash out unused PTO at the end of the year. These additional benefits can help to attract and retain employees.
Overall, PTO is an important aspect of an employee's compensation package and can have financial and tax implications for both the employee and the employer. Proper accounting and management of PTO can ensure that employees are accurately compensated and that companies can effectively track and control their expenses related to paid time off.
Valuation and Reporting of Fringe Benefits
Fringe benefits are non-cash compensation provided to employees in addition to their regular wages or salary. These benefits, also known as perks or job incentives, can take various forms such as health insurance, retirement plans, childcare assistance, company cars, gym memberships, and more.
When it comes to accounting for fringe benefits, it is essential to properly value and report them. The value of these benefits is generally included in an employee's gross pay and subject to income tax withholding. However, there might be certain deductions or exemptions available depending on the type of benefit.
Valuing fringe benefits can be a complex process as their worth needs to be determined accurately. Some benefits, such as health insurance or retirement plans, can be valued based on the premiums paid by the employer. On the other hand, non-monetary benefits like the use of company cars or gym memberships might require a fair market value assessment.
Reporting fringe benefits correctly is crucial for both the employer and the employee. Employers need to report the value of these benefits on an employee's Form W-2, which is used to report wages and taxes withheld. Employees should review their Form W-2 to ensure the accuracy of the reported benefits and to understand the impact on their taxable income.
In conclusion, the valuation and reporting of fringe benefits play a significant role in the accounting process. Employers must accurately assess the value of these benefits and properly report them for payroll and tax purposes. Employees should be aware of the benefits they receive and understand how they can affect their overall income and tax liabilities.
Determining the Value of Fringe Benefits
Fringe benefits are additional perks or incentives that employees receive in addition to their salary. These benefits can take many forms, including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other non-cash benefits.
When it comes to determining the value of fringe benefits for accounting purposes, employers must consider various factors. One important factor is tax withholding. Certain fringe benefits may be subject to taxes, such as Social Security and Medicare taxes. Employers must calculate and withhold these taxes based on the value of the benefits provided to employees.
In addition to tax withholding, employers also need to consider the impact of fringe benefits on employees' overall compensation. Fringe benefits can have a significant impact on an employee's take-home pay and overall financial situation. It is important for employers to properly account and report these benefits to ensure accurate calculations of employees' gross pay and deductions.
To determine the value of fringe benefits, employers must carefully assess the costs associated with providing these benefits. This includes not only the actual expenses incurred by the employer, such as insurance premiums or retirement plan contributions, but also any administrative costs or fees involved in managing these benefits.
Employers should also consider the value that employees place on fringe benefits. Some employees may highly value certain benefits, such as a comprehensive health insurance plan or a generous retirement plan, while others may place more importance on other forms of compensation, such as higher wages or bonuses.
In summary, determining the value of fringe benefits requires careful consideration of various factors, including tax withholding, overall compensation, and the costs associated with providing these benefits. By properly accounting for and valuing fringe benefits, employers can ensure accurate reporting and calculation of employees' income and deductions.
Recording Fringe Benefits in Financial Statements
When it comes to employee compensation, fringe benefits are an important aspect to consider. Fringe benefits are additional perks or incentives that an employee receives alongside their salary or wages. These benefits can include things like health insurance, retirement plans, vacation days, and more. It's crucial for companies to accurately record and report these benefits in their financial statements to provide a comprehensive picture of their employee compensation expenses.
Recording fringe benefits in financial statements typically requires a thorough understanding of accounting principles and regulations. Companies must carefully track and document the value of each fringe benefit provided to employees. This can involve calculating the cost of insurance premiums, employer contributions to retirement plans, and the value of paid time off.
Once the value of the fringe benefits has been determined, they are recorded as expenses in the company's financial statements. These expenses are often categorized separately from regular wages and salaries on the income statement. They may also be included as part of the total employee compensation expenses or listed as a separate line item.
In addition to recording the expenses, companies are also responsible for withholding any necessary taxes from employees' paychecks related to fringe benefits. This can include deductions for healthcare premiums or contributions to retirement plans. These withheld amounts must be properly accounted for and reported to the appropriate tax authorities.
Accurately recording fringe benefits in financial statements is essential for transparency and compliance. It allows stakeholders, such as investors and regulators, to understand the true cost of employee compensation and the financial health of the organization. Effective management of fringe benefits can also contribute to employee satisfaction and retention, making them a critical aspect of a company's accounting processes.
Reporting Fringe Benefits to Employees
When it comes to reporting fringe benefits to employees, it is essential for employers to ensure transparency and accuracy. Fringe benefits are additional incentives provided by the employer to the employee, which can include things like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. These benefits, though not part of the employee's salary, are still considered part of their overall compensation package.
When an employee receives a fringe benefit, it is important that the value of the benefit is accurately reported. This can be done through various means, such as including the value of the benefit on the employee's pay stub or through a separate statement. The employee should have a clear understanding of the value and nature of the fringe benefit they are receiving.
Employers also need to ensure that proper withholding is done for taxes and other deductions related to fringe benefits. Fringe benefits are generally subject to tax withholding, just like regular salary payments. The proper amount should be deducted from the employee's gross pay, taking into account any applicable tax rates and benefit limits.
In addition to taxes, employers may also need to report fringe benefits for other purposes, such as insurance coverage. Some fringe benefits, like health or life insurance, may require additional reporting for insurance purposes. This information can be included in the employee's annual benefits statement or provided separately.
Transparent reporting of fringe benefits is essential for both employers and employees. It allows employees to fully understand the value of their compensation package and make informed decisions about their job and future. Employers also benefit from accurate reporting, as it helps them comply with accounting and tax regulations, and ensures that employees have complete and accurate information about their income and benefits.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Compliance with various laws and regulations is a crucial part of accounting for fringe benefits. It is important for businesses to ensure that they meet all legal requirements surrounding these fringe benefits to avoid any penalties or legal issues.
When it comes to expenses, compensation, and income, businesses must fully disclose and accurately report any fringe benefits provided to employees. This includes benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, company cars, and other perks that employees receive as part of their employment. Failing to properly account for these benefits can lead to legal consequences.
Additionally, businesses must consider the tax implications of fringe benefits. Fringe benefits are often subject to taxes, both on the employer and employee side. Employers may be required to withhold and pay payroll taxes on the value of the fringe benefits, while employees may have to include the value of those benefits in their gross pay for income tax purposes.
Proper accounting and record-keeping are essential in order to accurately track and report fringe benefits. This includes maintaining detailed records of the types of benefits provided, the value of those benefits, and any deductions or incentives that may apply. These records enable businesses to demonstrate compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and ensure accuracy in their financial reporting.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to compliance and legal considerations surrounding fringe benefits is crucial for businesses. By understanding the various laws and regulations, accurately accounting for these benefits, and maintaining proper records, businesses can ensure they meet legal requirements and avoid any legal issues or penalties related to fringe benefits.
Compliance with Employment Laws
As an employer, it is essential to ensure compliance with employment laws regarding fringe benefits and compensation. Fringe benefits are additional forms of income provided to employees beyond their regular wages or salaries. These benefits can include incentives, insurance coverage, and other perks.
When accounting for fringe benefits, it is crucial to consider how they impact an employee's income and deductions. Fringe benefits are subject to payroll taxes and may require employers to withhold a portion of an employee's salary for taxes and insurance expenses.
Complying with employment laws involves accurately reporting fringe benefits on employee pay stubs and tax forms. Employers must track and document the value of fringe benefits provided to employees for tax reporting purposes.
Failure to comply with employment laws can result in penalties and legal consequences for employers. It is essential to have a solid understanding of the relevant laws and regulations and to ensure that all necessary accounting procedures are in place to accurately report and account for fringe benefits.
Overall, compliance with employment laws regarding fringe benefits is integral to maintaining a fair and legal working environment. Properly handling these benefits not only ensures appropriate tax withholding and reporting but also helps attract and retain quality employees by offering competitive benefits.
Documentation and Recordkeeping Requirements
In the field of accounting, proper documentation and recordkeeping are essential for maintaining accurate financial records and compliance with regulations. For expenses related to wages, income, and compensation, it is important to maintain thorough documentation such as pay stubs, employment contracts, and invoices. These documents provide evidence of the amounts paid, the nature of the expenses, and the individuals or entities involved.
When it comes to documenting incentives, perks, and fringe benefits provided to employees, it is necessary to keep detailed records. This may include records of salary calculations, bonus calculations, profit-sharing arrangements, and any other forms of compensation beyond the regular wages. The documentation should clearly outline the specific elements of each type of benefit for accurate accounting and reporting purposes.
Payroll documentation should also include records of deductions made from the employees' gross pay, such as taxes, insurance premiums, and other withholdings. These records are crucial for ensuring compliance with tax laws and other relevant regulations. They also serve as a reference for employees' net pay calculations and can be used for verification purposes in case of disputes or audits.
Recordkeeping requirements for fringe benefits also extend to the reporting of taxes. Proper documentation of any tax obligations related to fringe benefits, including employer contributions and employee withholdings, is essential. This may include records of calculations, tax forms, and statements from tax authorities. These records not only ensure accurate accounting but also support the employee's tax reporting and facilitate the reconciliation of financial information between the employer and the tax authorities.
In summary, documentation and recordkeeping are critical in the field of accounting, particularly when it comes to documenting expenses, wages, income, compensation, incentives, perks, and fringe benefits. Accurate recordkeeping ensures compliance with regulations, supports payroll calculations, facilitates tax reporting, and allows for proper accounting and financial management.
Auditing and Internal Controls for Fringe Benefits
In the realm of accounting, fringe benefits are an important aspect of employee compensation. They include perks such as insurance, retirement plans, and vacation time, in addition to wages and salary. As an auditor, it is crucial to ensure that these benefits are accurately recorded and reported.
One key area to focus on when auditing fringe benefits is the proper allocation of taxes. Employers must withhold taxes from an employee's gross pay, including any fringe benefit contributions. This requires accurate calculations and documentation to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Internal controls play a vital role in managing fringe benefits. It is important to establish and maintain controls to prevent fraud or abuse of these benefits. This may involve regularly reconciling payroll and benefits records, conducting periodic audits to detect any discrepancies or errors, and implementing a system of approvals and reviews for benefit-related transactions.
Another aspect of auditing and internal controls for fringe benefits involves ensuring that the correct deductions and incentives are applied. For example, an employee may be eligible for certain tax deductions related to health insurance contributions or retirement plan contributions. Auditors need to verify that these calculations are accurate and that the appropriate incentives are applied.
In summary, auditing and maintaining internal controls for fringe benefits are essential for accurate accounting and compliance with tax regulations. With careful attention to detail and the implementation of robust controls, businesses can ensure that their employees receive the appropriate compensation and benefits, while also meeting their financial reporting obligations.
Fringe Benefits vs. Salary: Pros and Cons
Gross pay: Fringe benefits and salary are two components of an employee's compensation package. Gross pay refers to the total amount of wages or salary an employee receives before any deductions are made.
Deductions: Salary is subject to various deductions, including income taxes, social security contributions, and other withholdings. Fringe benefits, on the other hand, may not be subject to the same level of taxation.
Benefits and perks: While salary is the regular payment an employee receives for their work, fringe benefits include additional perks such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other non-monetary benefits.
Wages and payroll: Salary is typically based on an employee's job responsibilities and can be paid on a monthly, bi-weekly, or annual basis. Fringe benefits are part of the employee's overall compensation and are often managed through the payroll system.
Insurance: One of the main advantages of fringe benefits is access to insurance coverage. These benefits may include health, dental, and vision insurance, as well as life and disability insurance. Salary alone may not provide the same level of coverage.
Job satisfaction: Fringe benefits can contribute to overall job satisfaction by providing employees with additional perks and incentives beyond their basic salary. This can help attract and retain talented individuals.
Expense considerations: While salary is a direct expense for the employer, fringe benefits can also add to the overall cost of employing an individual. However, offering competitive fringe benefits can be seen as an investment in the employee's well-being and loyalty.
Tax implications: Salary is typically subject to income taxes, while some fringe benefits may be tax-free or tax-deferred. This can result in additional tax savings for both the employer and the employee.
Overall compensation: When considering the pros and cons of fringe benefits vs. salary, it's important to look at the overall compensation package. The combination of salary and fringe benefits can provide a comprehensive package that meets both the financial and non-financial needs of employees.
Advantages of Offering Fringe Benefits
Offering fringe benefits to employees can have several advantages for both the employer and the employee. Below are some of the key benefits of providing fringe benefits:
- Attract and Retain Talented Employees: Offering fringe benefits can help companies attract and retain qualified and talented employees. In today's competitive job market, employees often consider more than just wages when evaluating job opportunities. The availability of appealing fringe benefits can give a company a competitive edge in attracting top talent.
- Increased Job Satisfaction: Providing fringe benefits can contribute to increased job satisfaction among employees. Fringe benefits can improve an employee's overall compensation package, making them feel valued and appreciated by their employer. This can lead to higher levels of employee morale, productivity, and loyalty.
- Tax Advantages: Certain fringe benefits can provide tax advantages for both employers and employees. For example, contributions made towards retirement plans or health insurance premiums may be tax-deductible for the employer. Employees may also enjoy tax savings on contributions made towards certain benefit plans.
- Improved Employee Health and Well-being: Fringe benefits such as health insurance or wellness programs can contribute to improved employee health and well-being. By providing access to affordable healthcare or encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, employers can help employees stay physically and mentally fit, reducing absenteeism and healthcare costs.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Offering fringe benefits can enhance employee engagement and motivation. When employees feel that their employer cares about their well-being and provides them with additional incentives, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work. This can lead to increased productivity and overall business success.
In conclusion, offering fringe benefits can be advantageous for both employers and employees. It can help attract and retain talented employees, increase job satisfaction, provide tax advantages, improve employee health and well-being, and enhance employee engagement. Employers should carefully consider the specific needs and preferences of their workforce to design a comprehensive fringe benefits package that meets the diverse needs of their employees.
Disadvantages of Offering Fringe Benefits
While offering fringe benefits can be a valuable tool for attracting and retaining employees, there are also some disadvantages to consider. One of the main disadvantages is the cost associated with providing these benefits. Fringe benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off can add up quickly, especially for a large workforce. These costs can eat into a company's profits and have a significant impact on the bottom line.
Another disadvantage is the administrative burden that comes with managing fringe benefits. Employers must keep track of employee deductions, handle any changes in benefits, and ensure compliance with various regulations. This can be time-consuming and require dedicated resources.
Furthermore, offering fringe benefits can complicate the payroll process. Fringe benefits are often subject to different tax rules and withholding requirements than regular wages. This means that employers must carefully calculate and report these benefits separately, which can increase the complexity of payroll and lead to potential errors if not handled correctly.
Additionally, employees may view fringe benefits differently depending on their individual needs and preferences. For example, an employee without dependents may not see the value in a comprehensive health insurance plan, while another employee may greatly appreciate this benefit. This can create challenges when designing a benefits package that appeals to all employees.
Lastly, offering fringe benefits can create inequities among employees. Some employees may receive more valuable fringe benefits than others, depending on their job level or tenure with the company. This can lead to feelings of resentment and dissatisfaction among employees, potentially affecting morale and productivity.
Best Practices for Managing Fringe Benefits
Managing fringe benefits is an important aspect of running a business. These benefits, such as insurance and income, are provided to employees in addition to their regular compensation. It is crucial to understand and properly account for these expenses in order to comply with tax regulations and ensure accurate financial reporting.
One of the best practices for managing fringe benefits is to clearly define what qualifies as a fringe benefit and communicate this to employees. This helps avoid confusion and ensures that only eligible expenses are included. It is also important to establish proper documentation and record-keeping procedures to support the provision of these benefits.
Another best practice is to clearly communicate the tax implications of fringe benefits to employees. Many fringe benefits are subject to taxes, including income tax and payroll taxes. Properly withholding and accounting for these taxes ensures compliance with tax laws and avoids penalties.
Deductions and exemptions are another important aspect of managing fringe benefits. Different benefits may have different tax treatment and eligibility requirements. Keeping track of these deductions and exemptions allows for accurate calculation of employee gross pay and correct withholding of taxes.
Incentives and perks can also be included as fringe benefits. These can vary widely and may include things like company cars, gym memberships, or flexible work hours. Properly accounting for and valuing these incentives is important for accurate financial reporting.
Overall, managing fringe benefits requires careful attention to detail and adherence to accounting principles. By properly defining, documenting, and communicating these benefits, businesses can ensure compliance with tax laws, accurate financial reporting, and employee satisfaction.
Developing a Comprehensive Fringe Benefits Policy
A fringe benefits policy is essential for any organization looking to effectively manage and account for its fringe benefit offerings. This policy serves as a comprehensive guide for both employers and employees regarding the various fringe benefits available. By outlining the specific benefits and their associated eligibility criteria, this policy helps establish clear guidelines for the administration and utilization of fringe benefits.
In the realm of accounting, fringe benefits refer to additional compensation provided to employees beyond their regular salary or wages. These benefits, often referred to as perks, can include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and various other supplemental offerings. Developing a robust fringe benefits policy ensures that all these benefits are properly accounted for and included in the employees' total compensation package.
In order to effectively manage and account for fringe benefits, it is crucial to integrate them into the payroll processes. This entails accurately calculating the value of fringe benefits and incorporating them into the employees' gross pay. By doing so, the organization can ensure that the appropriate deductions, such as taxes and insurance premiums, are applied to the employees' compensation.
Additionally, a comprehensive fringe benefits policy should address the employer's obligations in terms of withholding the necessary taxes from the employees' income. This includes providing clear guidelines for calculating and remitting the appropriate amount of taxes based on the employees' total compensation, including salary and fringe benefits.
Moreover, a well-structured fringe benefits policy can act as a tool for attracting and retaining top talent by offering attractive incentives. This can include provisions for career development opportunities, flexible work arrangements, or even non-monetary benefits such as employee recognition programs and wellness initiatives. By clearly outlining these benefits, the organization can showcase its commitment to employee well-being and job satisfaction.
Finally, a comprehensive fringe benefits policy should address the reporting and disclosure requirements related to fringe benefits expenses. This ensures transparent accounting practices and compliance with regulatory standards. It also helps the organization accurately report the total cost of fringe benefits provided to employees, which can be a significant expense for many organizations.
In conclusion, developing a comprehensive fringe benefits policy is crucial for effective accounting and management of fringe benefits. By establishing clear guidelines for the administration and utilization of these benefits, organizations can ensure accurate compensation calculations, compliance with tax regulations, and the attraction and retention of top talent.
Communicating Fringe Benefits to Employees
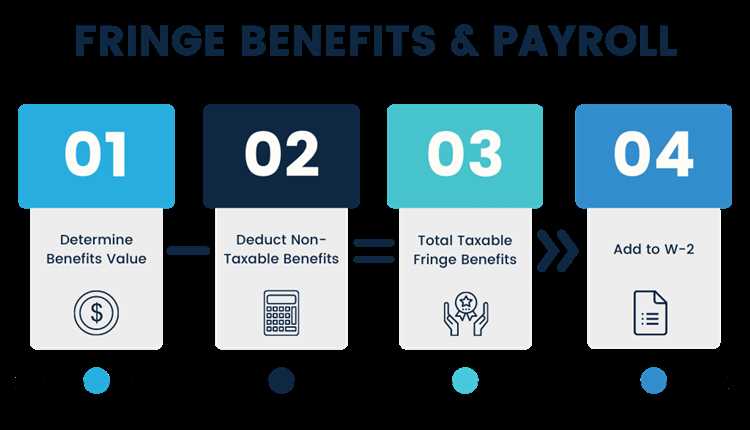
One of the key responsibilities of accounting and payroll departments is to effectively communicate fringe benefits to employees. Fringe benefits are additional forms of compensation that an employer provides to their employees, beyond their regular wages or salary. These benefits can include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other incentives.
When employees understand the value of the fringe benefits they receive, it helps them to better appreciate the comprehensive compensation package their employer provides. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and loyalty. Therefore, it is crucial for the accounting and payroll departments to effectively communicate these benefits to employees.
One way to communicate fringe benefits is through the employee's paycheck. Deductions for fringe benefits are typically listed separately from regular wages on the paycheck, so employees can easily see how these benefits contribute to their total compensation. Additionally, employees can review their year-end pay statements, which provide a summary of their wages, taxes, and deductions, including fringe benefits.
In addition to paycheck communication, employers can use other methods to communicate fringe benefits to employees. This might include informational brochures or handouts that provide details about each specific benefit, such as the coverage provided by health insurance or the vesting schedule for retirement plans. By providing clear and concise information, employees can make informed decisions about their benefits.
Employers may also consider holding informational sessions or workshops to educate employees about their fringe benefits. These sessions can cover how to enroll in various benefit programs, how to navigate the insurance claims process, and what resources are available for employee assistance. This type of direct communication can help employees feel more confident and empowered in utilizing their fringe benefits.
Overall, effective communication of fringe benefits is essential for both employees and employers. By understanding and appreciating their comprehensive compensation package, employees can make the most of their benefits while also feeling valued and supported in their work. For employers, communicating fringe benefits can help attract and retain top talent, foster a positive work culture, and ensure compliance with relevant accounting and tax regulations.
Monitoring and Evaluating Fringe Benefits Programs
Monitoring and evaluating fringe benefits programs is an essential part of effective accounting and financial management. Fringe benefits, such as insurance, expenses, and incentives, are additional compensations provided by employers to employees alongside their regular wages or salary. These benefits can include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks that enhance an employee's overall compensation package.
When it comes to monitoring fringe benefits programs, payroll administrators play a crucial role. They must accurately calculate and deduct the appropriate amount of taxes, withholdings, and other expenses from an employee's gross pay to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and company policies. This ensures that both the employer and employee are meeting their respective obligations.
In addition to payroll administrators, human resources personnel are responsible for monitoring and evaluating fringe benefits programs. They ensure that employees are aware of the available benefits and that they are properly enrolled and receive the benefits they are entitled to. They also evaluate the overall effectiveness of the programs and make adjustments as necessary to meet the changing needs of the workforce.
Accounting professionals also play a critical role in monitoring and evaluating fringe benefits programs. They track and record the expenses associated with providing these benefits, ensuring that they are accurately accounted for in the company's financial statements. This allows the company to assess the impact of fringe benefits on its overall financial performance and make informed decisions regarding the allocation of resources.
Monitoring and evaluating fringe benefits programs is not only important for compliance and financial management purposes, but it also helps to attract and retain top talent. Competitive fringe benefit programs can serve as a powerful recruitment and retention tool, as they provide employees with additional incentives to continue their employment with the company. Regular evaluation ensures that the company's benefits package remains competitive and aligns with industry standards.
In conclusion, monitoring and evaluating fringe benefits programs is a multifaceted task that involves various stakeholders, including payroll administrators, human resources personnel, and accounting professionals. It ensures compliance with regulations, assesses the financial impact, and helps attract and retain talented employees. By actively managing these programs, companies can demonstrate their commitment to employee well-being and create a positive work environment.
Future Trends in Fringe Benefits
As the workplace landscape evolves, so do the employee expectations for fringe benefits. Gone are the days when a traditional salary was enough to attract and retain top talent. Today, employees are looking for more than just a paycheck from their job.
One future trend in fringe benefits is an increased focus on wellness incentives. With rising healthcare costs and a growing emphasis on work-life balance, employers are recognizing the importance of providing employees with health and wellness benefits. From gym memberships to wellness programs and on-site healthcare facilities, these perks not only promote a healthy lifestyle but also have the potential to reduce healthcare expenses for both employees and employers.
Another emerging trend is the customization of fringe benefits. The one-size-fits-all approach is no longer sufficient. Employees have different needs and preferences, and they value flexibility in their benefits package. As a result, employers are offering a range of choices to cater to individual preferences. This could include options for different types of insurance coverage, retirement plans, and even unique perks such as student loan repayment assistance or pet-friendly workplaces.
With the rise of remote work and the gig economy, employers are also reevaluating their fringe benefits to meet the needs of these non-traditional workers. This includes offering flexible scheduling, remote work options, and opportunities for professional development and upskilling. Additionally, employers are exploring alternative compensation structures such as profit-sharing and stock options to align the incentives of employees with the long-term growth and success of the company.
In terms of accounting and taxes, the future of fringe benefits lies in increased automation and integration with payroll systems. This streamlines the process of administering and reporting fringe benefits, ensuring accurate and timely deductions and withholding. Additionally, advances in technology may allow for more efficient tracking of fringe benefits, simplifying the process of calculations and reconciling. Overall, the future of fringe benefits is a more personalized, flexible, and integrated approach that aligns with the evolving needs and expectations of employees.
Adoption of Flexible and Remote Work Policies
In today's modern work environment, the adoption of flexible and remote work policies has become increasingly common. These policies allow employees to have more control over their work schedule and location, providing them with a range of benefits.
One of the main advantages of adopting flexible and remote work policies is the ability to attract and retain top talent. Employees value the flexibility to choose when and where they work, and companies that offer these arrangements are often seen as more attractive employers.
From an accounting perspective, adopting flexible and remote work policies can also result in various impacts. For instance, fringe benefits such as telecommuting allowances, home office supplies, or equipment subsidies may need to be considered. These benefits are not subject to deductions or withholding taxes and should be included in payroll and compensation calculations.
Furthermore, adopting flexible and remote work policies can have implications for employee wages and income. In some cases, remote employees may be eligible for tax incentives or deductions related to home office expenses, insurance, or travel. Additionally, gross pay calculations may need to take into account any applicable taxes or withholdings.
Overall, the adoption of flexible and remote work policies requires careful accounting consideration. Companies should ensure that their payroll systems and practices are able to accommodate the various aspects of remote work, including factoring in any additional expenses or benefits provided to employees. By understanding the accounting implications, businesses can effectively manage their employee compensation while also meeting their obligations in terms of taxes and regulations.
Emphasis on Employee Wellness Programs
Employee wellness programs have become an important aspect of modern work environments. Companies are now recognizing the value of investing in the well-being of their employees. These programs are designed to promote and support the physical, mental, and emotional health of employees.
Employee wellness programs offer various benefits to employees, including improved work-life balance, increased job satisfaction, and reduced stress. They can also lead to higher productivity and lower turnover rates. These programs can include a wide range of initiatives such as fitness classes, mental health counseling, stress management workshops, and healthy eating programs.
From an accounting perspective, employee wellness programs are considered fringe benefits. Fringe benefits are additional benefits given to employees in addition to their wages or salaries. These benefits are not directly related to the job itself, but they are provided to enhance the overall compensation package.
The costs associated with employee wellness programs are considered expenses for the company. These expenses include the cost of implementing and maintaining the program, as well as the costs of any incentives or perks offered to employees. These expenses are typically included in the company's payroll and are subject to taxes and withholdings.
Accounting for fringe benefits in payroll involves calculating the value of the benefits and deducting them from the employee's gross pay. The remaining amount after deductions is the employee's net pay, which is the actual amount they receive as compensation. The company is responsible for reporting and paying the appropriate taxes on the fringe benefits provided.
In conclusion, employee wellness programs have become an important aspect of modern work environments. From an accounting perspective, these programs are considered fringe benefits and are subject to taxes and deductions. Investing in employee wellness can have various benefits for the company, including increased productivity and job satisfaction.
Integration of Technology in Fringe Benefits Administration
In today's digital age, the integration of technology has revolutionized the way companies manage their fringe benefits administration. Technology has streamlined and automated many processes, saving time and resources for organizations and their employees.
One area where technology has had a significant impact is in the management of employee income and expenses. With the use of advanced payroll accounting software, companies can easily track and calculate fringe benefit deductions from employee wages. This eliminates the need for manual calculations and ensures accurate and efficient processing.
Furthermore, technology has also facilitated the administration of various types of fringe benefits, such as insurance, perks, and incentives. With the help of online platforms and mobile applications, employees can access and manage their fringe benefits, making it convenient and user-friendly.
Moreover, technology has enabled better monitoring and reporting of fringe benefit programs. Companies can generate detailed reports, providing insights into the utilization and effectiveness of different benefits. This information can help organizations make informed decisions about their fringe benefit offerings and allocate resources effectively.
Additionally, technology has also improved the compliance aspect of fringe benefits administration. Automated systems can calculate and withhold the appropriate taxes and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. This reduces the risks of non-compliance and potential legal issues.
In conclusion, the integration of technology has transformed the administration of fringe benefits. It has simplified processes, increased efficiency, and improved the overall employee experience. By leveraging technology, organizations can effectively manage their fringe benefits programs, ensuring that employees are adequately rewarded for their hard work and dedication.